Bearing calculator - bearing finder
Manufacturers, like RBC Bearings®, provide a wide array of rolling-element bearing options that can be customized for multiple different use cases across industries, including food and beverage processing, mining, general manufacturing, material handling, transportation, aerospace, and more.
Under normal driving conditions, wheel bearings should last 85,000 to 100,000 miles. They can fail for several reasons, including:
Wheel bearingreplacementcostNear Me
Industrial ball bearings are used in various machinery and manufacturing equipment to facilitate smooth and efficient rotational motion. The bearing itself consists of an outer ring, an inner ring, a set of steel balls, and a cage that keeps the balls evenly spaced. Both the outer and inner rings are usually made of incredibly durable materials, such as steel or ceramic, which are designed to withstand high speeds and heavy loads.
Cheapwheel bearing repairnear me
It’s important to note that, unlike roller bearings, ball bearings operate on a point contact, meaning that they have a very small contact area with the load. This provides a low amount of friction, making ball bearings a great option for applications that require speed, as well as smooth rotational motion.
Frontwheel bearingreplacementcostNear me
We are no longer supporting IE (Internet Explorer) as we strive to provide site experiences for browsers that support new web standards and security practices.
Not sure which bearing type is right for your application? For further guidance, contact our knowledgeable team to discuss options that would best suit your needs.
Most notably, industrial roller bearings have a line contact instead of a point contact, which means they offer a greater surface area than ball bearings. This allows roller bearings to take on larger capacities and higher shock resistance without deforming or failing, unlike ball bearings, which can fail after a set number of revolutions.
Roller bearings are much more limited in movement; therefore, they are not the primary option for axial loads. They’re also made for a higher level of precision in most applications, which makes them more prone to angular misalignment in comparison to ball bearings.
Driving on a bad or failing wheel bearing is dangerous. If ignored, it can quickly turn into a safety issue and an expensive repair.
How much does wheel bearing repair costnear me
The steel balls within the bearing provide low-friction contact points between the inner and outer rings, enabling movement with minimal resistance and reducing energy lost to friction. The cage of the bearing serves to maintain the proper positioning of the balls, preventing them from touching each other and ensuring uniform distribution of the load.
Ball bearings feature a rolling element in the form of spherical balls, which are commonly used in small wheels and hard drives. One of the main benefits of ball bearings is that they are very versatile, as they can rotate on more than one axis. They are also designed for multiple load cases, including pure radial loads, pure axial loads, and combined radial and axial loads.
However, full-complement ball bearing designs do offer a solution for increasing radial-load capacity. Ball bearings are also more forgiving when it comes to misalignments than roller bearings.
Wheel bearing repairnear me
The average cost to replace a sealed wheel hub bearing is around $350 per wheel. However, depending on the make and model, the shop labor rate ($47 to $215 per hour, according to AAA) and any additional damage could push the cost beyond $1,000 per wheel.
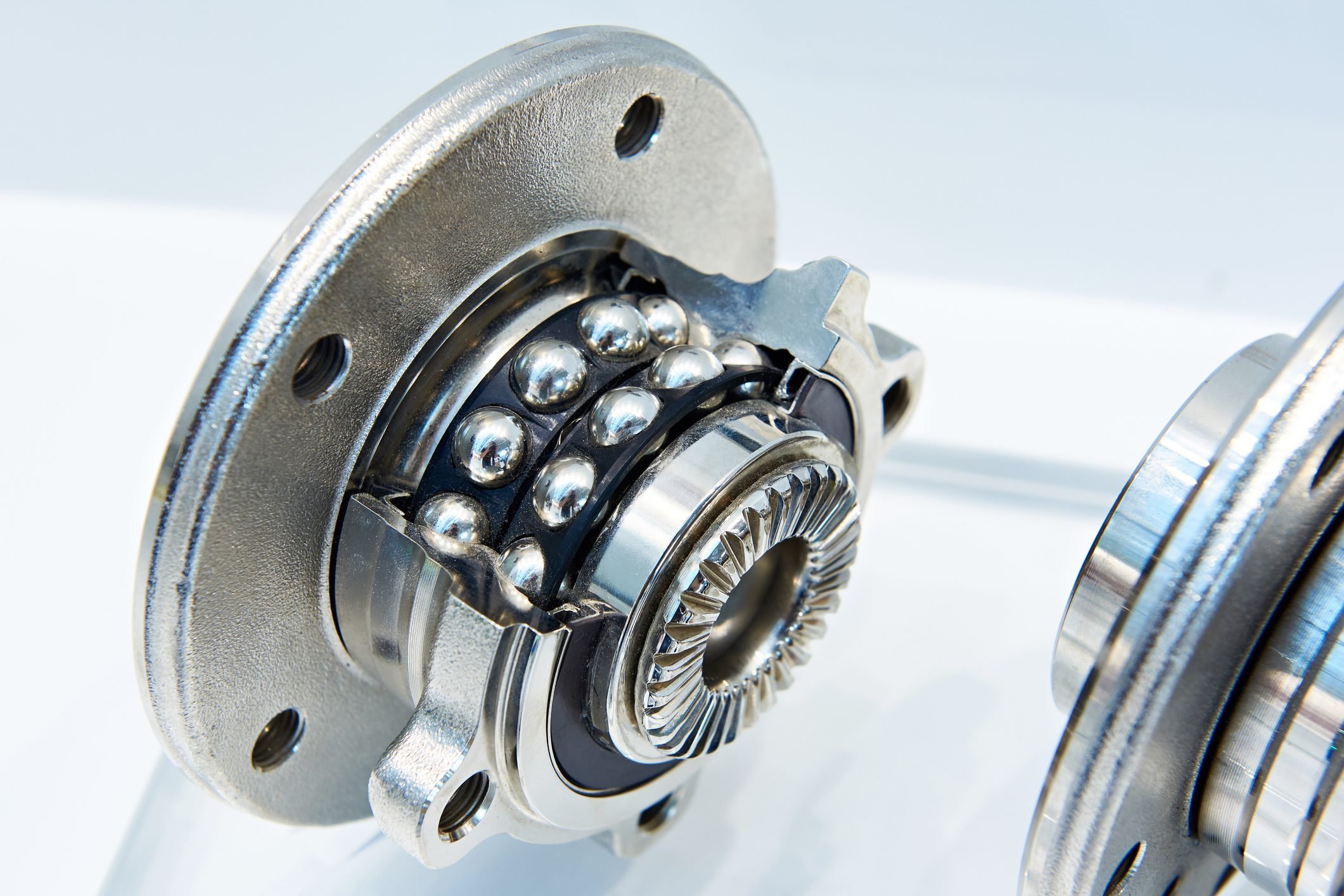
The cage and rollers are held together inside a hardened metal ring called a “race.” The seal keeps grease in and damaging water and debris out. Wheel bearings are installed inside, and secured to, the suspension, either by press-fit, bolts or a snap-ring. Once mounted, the wheel bearing rides on the axle shaft, allowing the tire/wheel to spin effortlessly.
My opinion? If your vehicle has more than 50,000 miles or has been driven in harsh conditions, then it’s logical to replacing wheel bearings on both axles. However, if your vehicle has low mileage and the other bearing is in good condition, replacing only the damaged bearing should not be a problem.
Wheel Bearing costAutoZone
On modern front- and four-wheel-drive cars, wheel bearings are a set of permanently sealed, precisely machined steel ball or straight roller bearings. The balls or rollers are encased in a “cage” that supports the bearings, allowing them to rotate freely.
Similar to ball bearings, industrial roller bearings are mechanical devices used to create smooth and efficient motion. However, rather than using a set of steel balls, a roller bearing uses cylindrical rollers to minimize friction.
Unlike ball bearings, roller bearings are available in more than just spherical shapes and have a fixed axis of rotation. In addition to spherical options, roller bearings are also available in cylindrical, tapered, and needle shapes. They are also available in full-complement designs to help with reciprocating motions.
I’ve replaced hundreds, if not thousands, of wheel bearings. One thing I’ve learned: A bad wheel bearing always gives an indication it’s failing. These include:
Frontwheel bearingreplacementcost
Never reuse any wheel bearing (sealed or tapered) that’s loose, worn, noisy or shows any signs of wear. Trying to fix a loose or damaged wheel bearing can result in an accident and severe injury. Even if a pro suggests repairing a bearing, don’t let them.
Products like RBC Bearings’ TP Series cylindrical roller thrust bearings are great for crane hooks, oil well swivels, and gearboxes, whereas their Pitchlign® caged heavy-duty needle roller bearings are ideal for cross head bearings applications.
Rearwheel bearingreplacementcost
As mentioned above, ball bearings are ideal for higher speeds and lighter loads, whereas roller bearings are better suited for heavier loads and shocks.
However, on some vehicles, it can be less than $100 per wheel. And you can save hundreds in labor if you DIY. If you don’t have the tools, most auto parts stores will lend you the specialty tools and equipment needed.
Older rear-wheel-drive cars or trailers use a set of two tapered roller bearings that face each other. These should be routinely serviced every 20,000 miles, or once a year.

When working with different applications, do you know the key differences between ball bearings vs. roller bearings? While these bearings both provide a rolling, anti-friction element and appear similar in style, their use cases are entirely different, especially when it comes to bearing weight.
The cylindrical rollers are positioned between an inner and outer ring and offer a larger contact surface area. They are evenly spaced and guided by a cage to maintain their relative positions. This design allows for greater load-carrying capacity, as well as enhanced axial and radial performance.

Due to their point contact, ball bearings do not operate the best under heavy loads. Because of this, they are primarily used in applications that have higher speeds and lighter loads
Products like RBC Bearings’ Nice® SRM Series™ precision-machined, single-row ball bearings would be perfect for material handling and packaging equipment. Thin section ball bearings from RBC Bearings also offer solutions and custom designs for the aerospace industry.
In my 50 years in the auto repair industry, I can’t recall one good story about wheel bearings. Most involve some sort of brake system failure, tires exploding, or fire from a seized red-hot bearing igniting axle grease. Bad wheel bearings should not be ignored.
Wheel bearings allow cars and trucks to run smoother and more efficiently by reducing friction and supporting vehicle weight.
To take a closer look at the advantages of each type, as well as when to choose one bearing over the other for a given application, we’ve put together a breakdown and comparison of these two types of bearings.
NOTE: Whether you DIY or your mechanic replaces the bearing, always install a new axle hub nut. Most hub nuts are prevailing torque fasteners. They’re used on critical components, like securing axle shafts to hub bearings, where a loose nut could lead to disastrous consequences.




 8613869596835
8613869596835