Bearings 101: Types, Failures, & Strategic Selection - bearing examples
By considering factors like bearing type, design, and operating conditions, engineers can ensure optimal performance and reliability while minimizing the risk of premature failure.
Axialandradialdirection
They come in various configurations, such as thrust roller bearings, thrust spherical roller bearings, and thrust tapered roller bearings.
Factors such as rotational speed, temperature, shock loads, and contaminants can affect the bearing's ability to handle axial forces.
Axial loadformula
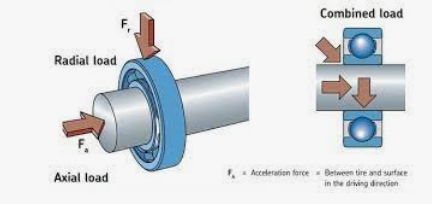
Radial load refers to the force applied perpendicular to the bearing's axis, causing the inner and outer races of the bearing to deform.
This phenomenon is known as "skidding" or "sliding" and can result in excessive wear, overheating, and premature bearing failure.
Radial loadexample
Operating Conditions:The operating conditions of an application can significantly impact the performance of ball bearings under axial loads.
Axial loadexample
Understanding the capabilities and limitations of ball bearings in handling axial loads is crucial for selecting the right bearing for specific applications.
Bearing Type:As mentioned earlier, angular contact and thrust ball bearings are better suited for handling higher axial loads than deep grooves and self-aligning ball bearings.
Angular contact ball bearings and thrust ball bearings are specifically designed to handle higher axial loads compared to deep grooves and self-aligning ball bearings.
discuss the factors influencing ball bearings' ability to handle axial loads and explore alternative bearing options for axial load applications.
Radial load vs axial loadbearing
While all ball bearings can handle some degree of axial load, the magnitude of the load they can withstand varies among different types.
Ball bearings are widely used in various mechanical applications because they reduce friction and support the rotational and linear motion.
Design and Construction: The design and construction of the ball bearing also play a crucial role in its ability to handle axial loads.
Radial load vsthrustload
Bearings with more contact points, larger balls, and optimized raceway profiles can distribute axial loads more effectively,
These bearings are suitable for applications with heavy axial and moderate radial loads, such as heavy-duty machinery and mining equipment.
Angular contact ball bearings and thrust ball bearings are designed with specific contact angles and raceway configurations to better handle axial loads.
Radial loadformula
Axial loads can cause the balls to move sideways along the raceway, leading to increased friction and potential failure of the bearing.
Radial loadbearing
Axial load, on the other hand, is applied parallel to the bearing's axis and can cause the balls to move along the raceway. Axial loads are encountered in applications with thrust or linear forces, such as pumps, compressors, or axial fans.
Cylindrical roller bearings are commonly used in applications such as rolling mills, gearboxes, and large industrial machinery.
Preload:Preload is the intentional introduction of internal clearance reduction in a bearing to enhance its ability to handle axial loads.
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings: Self-aligning ball bearings are designed to accommodate misalignment between the shaft and the housing.




 8613869596835
8613869596835