Class N | Thomson | International - 1.2498 x 4
TK41
The tables provided are design recommendation and should not supercede ABEC, ISO or OEM recommended fits and tolerances.
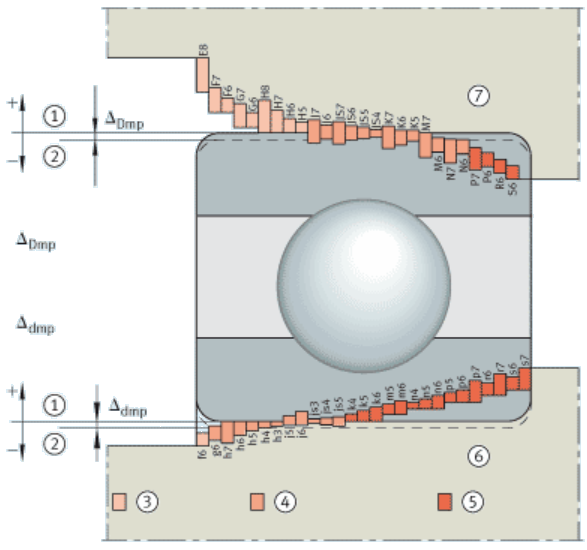
Bearing Engineering and Knowledge Application Menu Tolerances, Engineering Design & Limits & Fits Bearing Shaft and Housing Installation Tolerances Size and fit tolerances for bearing mating shafts and housing are provided within the tables below are defined by ISO tolerances for shafts and housings (ISO 286) in conjunction with the tolerances Îdmp for the bore and ÎDmp for the outside diameter of the bearings per. (DIN 620). The tables provided are design recommendation and should not supercede ABEC, ISO or OEM recommended fits and tolerances. Tolerance zones amd variability The ISO tolerances are defined in the form of tolerance zones. They are determined by their position relative to the zero line (= tolerance position) and their size (= tolerance grade, see ISO 286). The tolerance position is indicated by letters (upper case for housings, lower case for shafts). For a schematic representation of the most common rolling bearing fits. The tables as below contain recommendations for the selection of shaft and housing tolerances that are valid for normal fitting and operating conditions. Tolerance specification deviations are possible if particular requirements apply, for example in relation to running accuracy, smooth running or operating temperature. Increased running accuracies thus require closer tolerances such as tolerance grade 5 instead of 6. If the inner ring is warmer than the shaft during operation, the seating may loosen to an impermissible extent. A tighter fit must then be selected, for example m6 instead of k6. In such cases, the question of fits can only be resolved by a compromise. The individual requirements must be weighed against each other and those fulfilled that give the best overall solution. Related: Preferred Tolerances Metric ISO 286 Table of Hole Bore Tolerances per. ISO 286 Calculator Table of Shaft Tolerances per. ISO 286 Calculator Roller Bearing Fits and Tolerances Designations (Click on image to enlarge) Zero line (Line-to-Line Fit) Nominal diameter Loose fit Transition fit Tight fit Shaft diameter Housing bore ÎDmp = tolerance for bearing outside diameter Îdmp = tolerance for bearing bore Shaft tolerances for radial bearings with cylindrical bore Condition of rotation Bearing type Shaft diameter mm Displacement facility Load Tolerance zone Point load on inner ring Ball bearings, roller bearings All sizes Inner ring easily displaced g6 (g5) Inner ring not easily displaced, angular contact ball bearings and tapered roller bearings with adjusted inner ring h6 (j6) Needle roller bearings All sizes Non-locating bearing h6 (g6)1) Circumferential load on inner ring or indeterminate load direction Ball bearings up to 50 Normal loads2 j6 (j5) 50 to 100 Low loads3 j6 (j5) Normal and high loads4) k6 (k5) 100 to 200 Low loads2 k6 (m6) Normal and high loads5 m6 (m5) over 200 Low loads m6 (m5) Normal and high loads n6 (n5) Roller bearings up to 60 Low loads j6 (j5) Normal and high loads k6 (k5) 60 to 200 Low loads k6 (k5) Normal loads m6 (m5) High loads n6 (n5) 200 to 500 Normal loads m6 (n6) High loads, shocks p6 over 500 Normal loads n6 (p6) High loads p6 Needle roller bearings up to 50 Low loads k6 Normal and high loads m6 50 to 120 Low loads m6 Normal and high loads n6 120 to 250 Low loads n6 Normal and high loads p6 250 to 400 Low loads p6 Normal and high loads r6 400 to 500 Low loads r6 Normal and high loads s6 over 500 Low loads r6 Normal and high loads s6 For easier fitting. C/P ï¼ 10 C/P ï¼ 12 C/P ï¼ 12 C/P ï¼ 10 Shaft tolerances for axial bearings Load Bearing type Shaft diameter Operating conditions Tolerance zone Axial load Axial deep groove ball bearings All sizes - j6 Axial deep groove ball bearings, double direction - k6 Axial cylindrical roller bearings with shaft locating washer - h6 (j6) Axial cylindrical roller and cage assemblies - h8 Combined load Axial spherical roller bearings All sizes Point load on shaft locating washer j6 up to 200 mm Circumferential load on shaft locating washer j6 (k6) over 200 mm k6 (m6) Housing tolerances radial bearings Condition of rotation Displacement facility Load Operating conditions Tolerance zone Point load on outer ring Outer ring easily displaced, housing un split The tolerance grade is determined by the running accuracy required H7 (H6)1) Outer ring easily displaced, housing split H8 (H7) Outer ring not easily displaced, housing un split High running accuracy required H6 (J6) Outer ring not easily displaced, angular contact ball bearings and tapered roller bearings with adjusted outer ring Housing split Normal running accuracy H7 (J7) Outer ring easily displaced Heat input via shaft G72) Circumferential load on outer ring or indeterminate load direction Low loads, outer ring cannot be displaced For high running accuracy requirements: K6, M6, N6 and P6 K7 (K6) Normal loads, shocks, outer ring cannot be displaced M7 (M6) High loads, shocks (C/P ï¼ 6), outer ring cannot be displaced N7 (N6) High loads, severe shocks, thin-walled housing, outer ring cannot be displaced P7 (P6) 1, G7 for housings made from flake graphite cast iron GG, if bearing outside diameter D ï¼ 250 mm and temperature difference between outer ring and housing ï¼ 10 K. 2, F7 for housings made from flake graphite cast iron GG, if bearing outside diameter D ï¼ 250 mm and temperature difference between outer ring and housing ï¼ 10 K. Housing tolerances for axial bearings Load Bearing type Operating conditions Tolerance zone Axial load Axial deep groove ball bearings Normal running accuracy High running accuracy E8 H6 Axial cylindrical roller bearings with housing locating washer - H7 (K7) Axial cylindrical roller and cage assemblies - H10 Axial spherical roller bearings Normal loads High loads E8 G7 Combined loads Point load on housing locating washer Axial spherical roller bearings - H7 Combined loads Circumferential load on housing locating washer Axial spherical roller bearings - K7 Source ISO 286 DIN 620 Related Shaft to Shaft Axial Alignment Design Tolerances Tables Housing Tolerance Classifications for Metric Radial Ball and Roller Bearings Shaft Tolerance Radial Ball and Roller Bearings GD&T Application Single Datum Axis - Two Datum Features General ISO Geometrical Tolerances Per. ISO 2768 Ball Bearings ABEC Standard Tolerances Data Bearing Types and Application Design | Ball Bearings | Roller Bearings | Thrust Bearings
1, G7 for housings made from flake graphite cast iron GG, if bearing outside diameter D ï¼ 250 mm and temperature difference between outer ring and housing ï¼ 10 K.
TK30
2, F7 for housings made from flake graphite cast iron GG, if bearing outside diameter D ï¼ 250 mm and temperature difference between outer ring and housing ï¼ 10 K.
© Copyright 2000 - 2025, by Engineers Edge, LLC www.engineersedge.com All rights reservedDisclaimer | Feedback Advertising | Contact
TK38
Home Engineering Book Store Engineering Forum Applications and Design Beam Deflections and Stress Bearing Apps, Specs & Data Belt Design Data Calcs Civil Engineering Design & Manufacturability Electric Motor Alternators Engineering Calculators Excel App. Downloads Flat Plate Stress Calcs Fluids Flow Engineering Friction Engineering Gears Design Engineering General Design Engineering Hardware, Imperial, Inch Hardware, Metric, ISO Heat Transfer Hydraulics Pneumatics HVAC Systems Calcs Economics Engineering Electronics Instrumentation Engineering Mathematics Engineering Standards Finishing and Plating Friction Formulas Apps Lubrication Data Apps Machine Design Apps Manufacturing Processes Materials and Specifications Mechanical Tolerances Specs Plastics Synthetics Power Transmission Tech. Pressure Vessel Pumps Applications Re-Bar Shapes Apps Section Properties Apps Strength of Materials Spring Design Apps Structural Shapes Threads & Torque Calcs Thermodynamics Physics Vibration Engineering Videos Design Manufacture Volume of Solids Calculators Welding Stress Calculations Training Online Engineering
TK42 flight Status
Tolerance specification deviations are possible if particular requirements apply, for example in relation to running accuracy, smooth running or operating temperature. Increased running accuracies thus require closer tolerances such as tolerance grade 5 instead of 6. If the inner ring is warmer than the shaft during operation, the seating may loosen to an impermissible extent. A tighter fit must then be selected, for example m6 instead of k6.
Johannesburg Airport
Size and fit tolerances for bearing mating shafts and housing are provided within the tables below are defined by ISO tolerances for shafts and housings (ISO 286) in conjunction with the tolerances Îdmp for the bore and ÎDmp for the outside diameter of the bearings per. (DIN 620).
This dialogue will close in 60 seconds or you can click the exit icon in the top right corner to go back to the flight map immediately. We appreciate you trying our new Live Surface Map feature. If you have a couple of minutes, we'd like to collect your feedback on it.
The ISO tolerances are defined in the form of tolerance zones. They are determined by their position relative to the zero line (= tolerance position) and their size (= tolerance grade, see ISO 286). The tolerance position is indicated by letters (upper case for housings, lower case for shafts). For a schematic representation of the most common rolling bearing fits.
In such cases, the question of fits can only be resolved by a compromise. The individual requirements must be weighed against each other and those fulfilled that give the best overall solution.
The tables as below contain recommendations for the selection of shaft and housing tolerances that are valid for normal fitting and operating conditions.




 8613869596835
8613869596835