Deep groove ball bearing fr6-2rs 9.5x22.2x7.1 mm seal on ... - fr6-2rs
Linear bearing
Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width OPEN = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width ZZ/2RS = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)
Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width OPEN = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width ZZ/2RS = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)
Bearing lookup
Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)
Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width OPEN = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width ZZ/2RS = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)
Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)
Bearing
Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)
Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)
Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)
Jota bearing CO., LTD

Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)
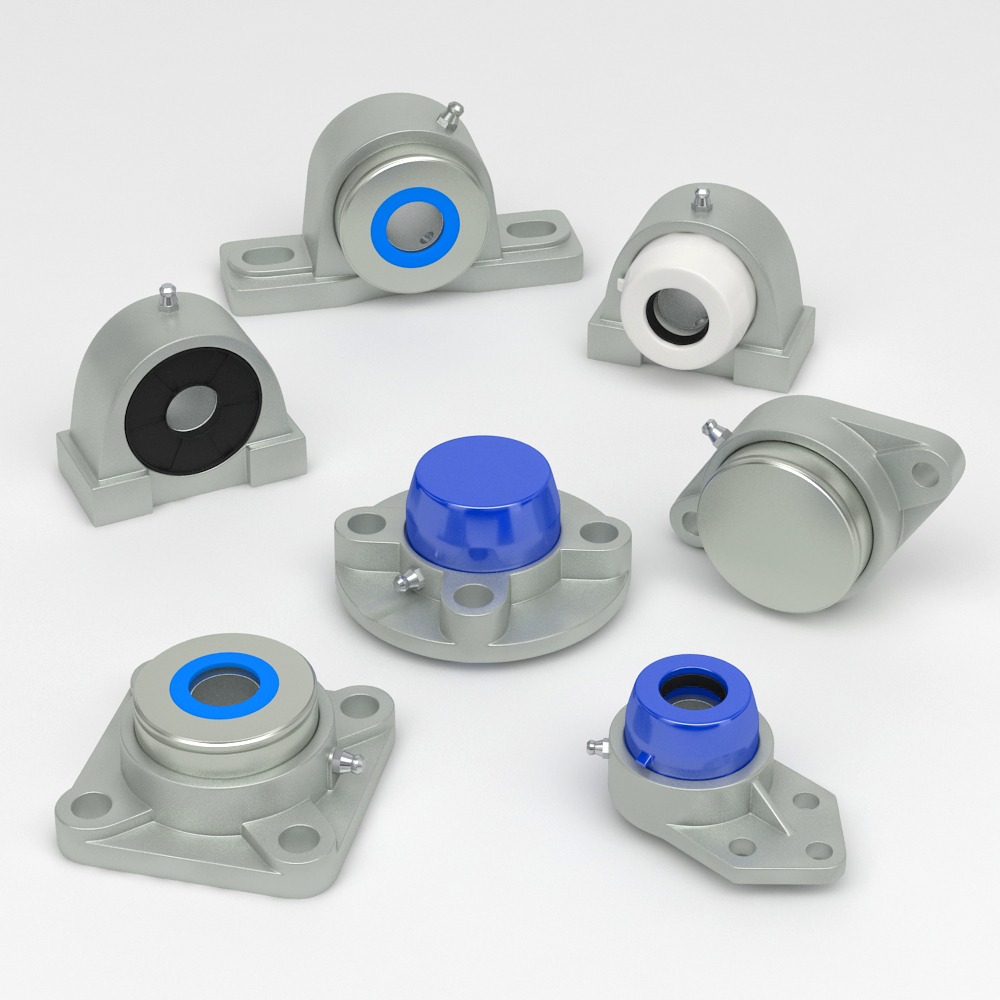
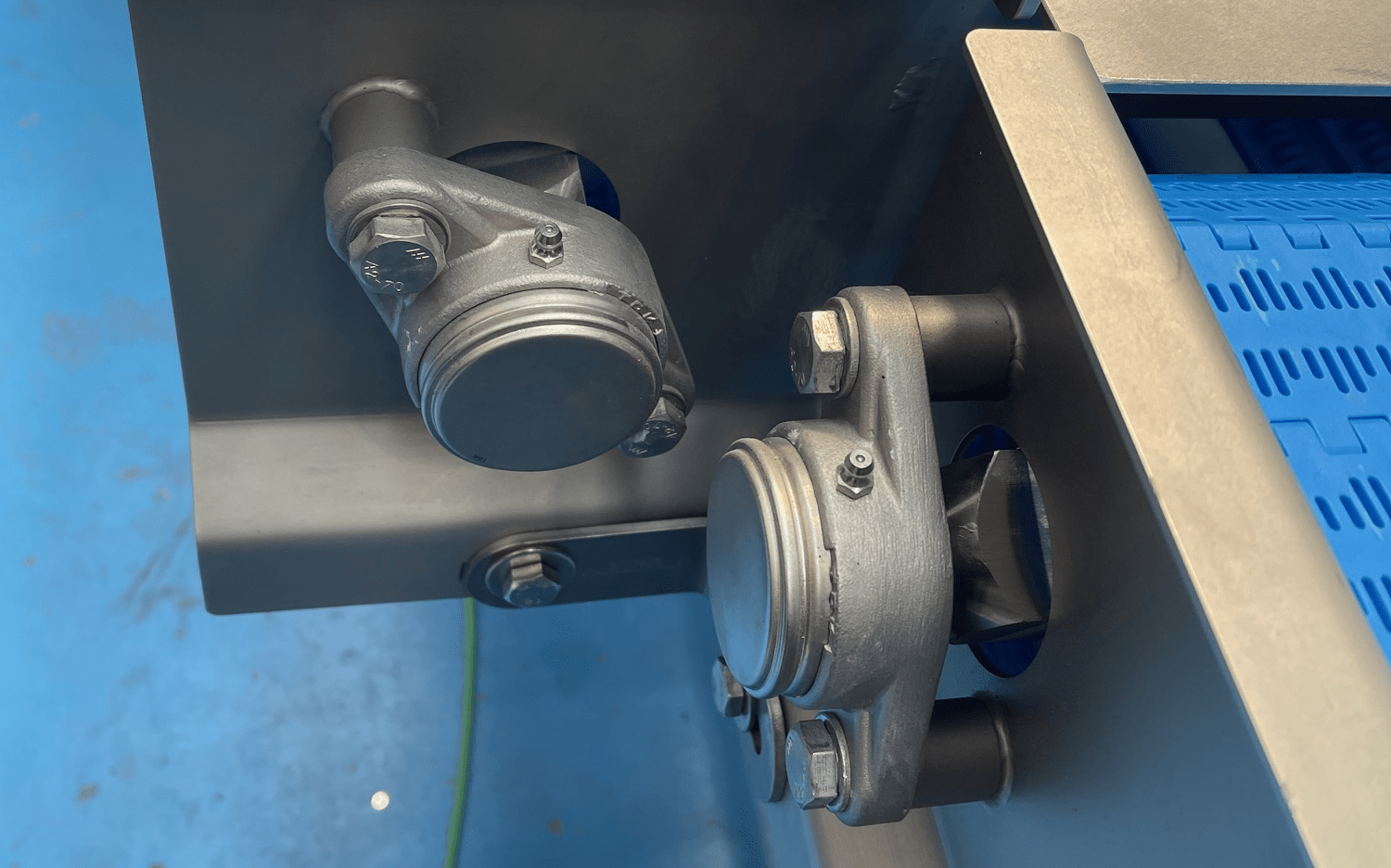
The choice between pillow block and flange bearing units depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the orientation of the shaft, load conditions, and alignment needs. Pillow block bearings are ideal for applications where the shaft runs parallel to the mounting surface and require easy installation and maintenance. In contrast, flange bearings are suited for perpendicular mounting and applications requiring precise alignment and support.
Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)
SKF bearing
Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)

SKF bearing Calculator
Pillow block bearing housing are designed for shafts parallel to the mounting surface and are typically mounted on horizontal bases, providing easy installation and maintenance. They are ideal for applications like conveyor systems and agricultural machinery, handling primarily radial loads.
Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)
SKF Bearing Select
Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)
Flange bearing housing, however, are designed for shafts perpendicular to the mounting surface, offering more mounting options with various flange shapes. They provide better alignment and support for applications like automotive and aerospace industries, capable of handling both radial and axial loads. Flange units are suited for applications requiring precise alignment and additional mounting stability.
Deep grooveballbearing
Pillow Block Bearing Housing Pillow block bearing housing are designed for shafts parallel to the mounting surface and are typically mounted on horizontal bases, providing easy installation and maintenance. They are ideal for applications like conveyor systems and agricultural machinery, handling primarily radial loads. Flange Bearing Housing Flange bearing housing, however, are designed for shafts perpendicular to the mounting surface, offering more mounting options with various flange shapes. They provide better alignment and support for applications like automotive and aerospace industries, capable of handling both radial and axial loads. Flange units are suited for applications requiring precise alignment and additional mounting stability. Product Line Contact 1. Mounting Configuration Pillow Block Bearing Units: Pillow block bearing units are designed for applications where the shaft is parallel to the mounting surface. They are typically mounted on a flat, horizontal surface. The housing of a pillow block is usually open on the top, making it easy to install and maintain the shaft. Flange Bearing Units: Flange bearing units are designed for applications where the shaft is perpendicular to the mounting surface. They are mounted using flanges, which can be in various shapes such as square, round, or oval. Flange units provide additional mounting options for situations where the support surface is vertical or at an angle. 2. Design and Structure Pillow Block Bearing Units: Consist of a bearing mounted inside a housing, which is shaped like a “pillow.” The design allows for easy installation and alignment. They often include a grease fitting for easy lubrication. Flange Bearing Units: Feature a bearing within a housing that has a flanged end. The flange provides multiple mounting points, which enhances stability and load distribution. They are used when additional support or alignment is needed at the mounting point. 3. Applications Pillow Block Bearing Units: Commonly used in conveyor systems, agricultural equipment, and packaging machinery. Ideal for applications requiring long shaft lengths with support at regular intervals. Flange Bearing Units: Widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and food processing. Suitable for applications that require precise alignment and support at the ends of the shaft. 4. Load Handling Pillow Block Bearing Units: Primarily designed to handle radial loads but can accommodate some axial loads depending on the design. They are effective in applications with consistent directional loads. Flange Bearing Units: Capable of handling both radial and axial loads due to their secure mounting and design. Their construction makes them suitable for complex load applications. 5. Installation and Maintenance Pillow Block Bearing Units: Generally easier to install and maintain due to their simple design. The open housing design allows for easy access during maintenance. Flange Bearing Units: May require more precise alignment during installation to ensure proper operation. Maintenance can be slightly more complex due to the enclosed design. 6. Flexibility and Alignment Pillow Block Bearing Units: Provide some flexibility in shaft alignment, which can be beneficial in systems where slight misalignment may occur. The design allows for minor adjustments during installation. Flange Bearing Units: Offer more rigid support and are less forgiving of misalignment. They provide better alignment in applications where precision is critical. The choice between pillow block and flange bearing units depends on the specific requirements The choice between pillow block and flange bearing units depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the orientation of the shaft, load conditions, and alignment needs. Pillow block bearings are ideal for applications where the shaft runs parallel to the mounting surface and require easy installation and maintenance. In contrast, flange bearings are suited for perpendicular mounting and applications requiring precise alignment and support. Questions and contact Contact us for hygienic solution Get our catalogue here Contact Articles 3. January 2025 Advantages of Using Conveyor Side Guides in Stainless Steel 3. January 2025 Where to Use Conveyor Side Guides in Stainless Steel 3. January 2025 Why Use Conveyor Side Guides in Stainless Steel 3. January 2025 The Role of Reinforced Side Guides in Sanitary Industries 24. December 2024 Benefits of Increasing Hygienic Inspection Points 24. December 2024 Easy Access and Serviceability in Sanitary Industries 24. December 2024 The Necessity of Simple, Durable and Reliable Hygienic Designs 18. December 2024 EHEDG Certified Components: Driving Sustainability 18. December 2024 Ease to Clean VS Maintenance Accessibility 14. December 2024 The Right Stainless Steel to Meet 3A-SSI Standards 14. December 2024 Choosing the Right Stainless Steel for Bearing Units 13. December 2024 Bearing Unit Engineering: The Role of 420 vs 440 Stainless Steel
Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)
Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width OPEN = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width ZZ/2RS = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)
Inner Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Outer Dimension = Boundary dimensions (mm) Width = Boundary dimensions (mm) Dynamic(Cr) = Basic load ratings (Lbf) Static(Cor) = Basic load ratings (Lbf)
Table of Contents: 6000 Metric Series6200 Metric Series6300 Metric Series6700 Metric Series6800 Metric Series6900 Metric Series600 Metric Series600 Metric Series (Flanged)MR Metric Series16000 Metric Series60/22 - 63/22 Metric Series62000 Metric Series5200 Metric Series5300 Metric SeriesR Inch Series1600 Inch Series




 8613869596835
8613869596835