IRFC: Home - 11134
The outer wheel bearing is usually held in place by a large nut. Using the appropriate socket, loosen and remove it. Gently pull out the wheel assembly, using a pry bar if needed.
Take your car for a test drive to make sure everything feels smooth and responsive. Pay considerable attention to any unusual noises, vibrations, or handling issues. It's normal for the new wheel bearings to require a short break-in period, so monitor their performance during the first few days of driving.
Lift the wheel you removed earlier and align it with the wheel studs. Tighten the lug nuts by hand in a crisscross pattern to ensure even tightening. Lower the vehicle using the floor jack and remove the jack stands. Utilize a torque wrench to tighten the lug nuts to the recommended torque specification.
Ultra-Glide™ 3/4" High Performance Ball Bearing Guide Assembly ; Mfr # 47709 ; Buy "your way". Order by 24/7 by web, contact our sales reps or call by phone. ; One ...
202429 — Types of roller bearings are cylindrical, needle, barrel, tapered, carb toroidal, cylindrical roller thrust, needle roller thrust, tapered roller thrust and ...
SKFbearing tolerancechart pdf
Wheel bearings typically last around 80,000 to 100,000 miles before they need to be replaced. However, it is recommended that you inspect your wheel bearings regularly and replace them if necessary as part of routine vehicle maintenance.
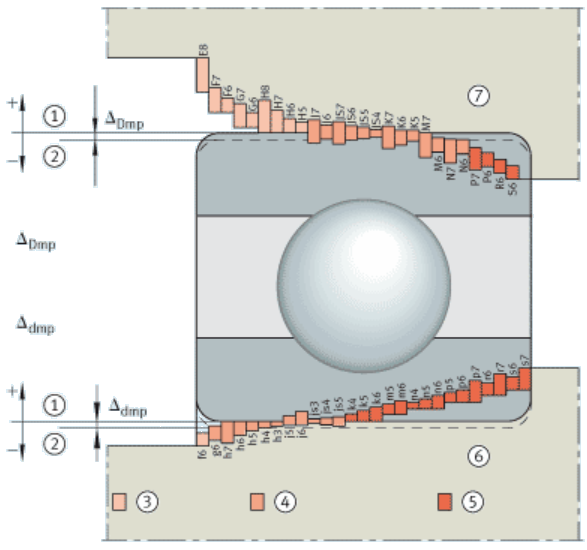
The ISO tolerances are defined in the form of tolerance zones. They are determined by their position relative to the zero line (= tolerance position) and their size (= tolerance grade, see ISO 286). The tolerance position is indicated by letters (upper case for housings, lower case for shafts). For a schematic representation of the most common rolling bearing fits.
If you need to replace the wheel bearings on multiple wheels, repeat the above steps for each wheel, ensuring you follow the same procedure for each one.
SNT Plummer Block bearing housing is designed to work in tough environments. The Timken® SNT line features 200, 300, 500 & 600 series housings.
In such cases, the question of fits can only be resolved by a compromise. The individual requirements must be weighed against each other and those fulfilled that give the best overall solution.
© Copyright 2000 - 2025, by Engineers Edge, LLC www.engineersedge.com All rights reservedDisclaimer | Feedback Advertising | Contact
Bearing tolerancecalculator
(4931) -
Ensure to park your vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake. Loosen the lug nuts on the wheel where you'll be replacing the wheel bearings, but do not remove them just yet. Place the floor jack in the designated lifting point (refer to your vehicle's manual) and raise the car until the wheel is off the ground. Secure the vehicle with jack stands for added safety.
Ballbearing tolerance table
Carefully remove the dust or grease cap from the wheel hub using a pry bar or screwdriver. This will expose the castle nut and cotter pin. Remove the cotter pin and unscrew the castle nut.
Ballbearing tolerancechart
Finally, always remember to observe safety precautions and follow the steps in this guide to ensure your ride runs as smoothly and efficiently as possible.
1, G7 for housings made from flake graphite cast iron GG, if bearing outside diameter D ï¼ 250 mm and temperature difference between outer ring and housing ï¼ 10 K.
The tables provided are design recommendation and should not supercede ABEC, ISO or OEM recommended fits and tolerances.
Replacing wheel bearings is a straightforward process that can be completed with the proper tools and materials. If you feel unsure or lack the necessary expertise, it's best to consult Goodhood mobile auto repair services for professional assistance.
Tolerance specification deviations are possible if particular requirements apply, for example in relation to running accuracy, smooth running or operating temperature. Increased running accuracies thus require closer tolerances such as tolerance grade 5 instead of 6. If the inner ring is warmer than the shaft during operation, the seating may loosen to an impermissible extent. A tighter fit must then be selected, for example m6 instead of k6.
Bearingshafttolerancechart
Bearing tolerance tablepdf
The tables as below contain recommendations for the selection of shaft and housing tolerances that are valid for normal fitting and operating conditions.
Apply a good amount of wheel bearing grease to the inner race of the new wheel bearings. Carefully place the bearings into the wheel hub, ensuring they are properly seated. Grease the outer race of the bearings and apply grease to the spindle as well.
40:15:35; 40.1535. Calculation Input. Base Antenna Latitude* Base Antenna Longitude* Remote ...
CF 3 SB MCGILL | Cam Follower and Track Roller - Stud Type 2300112000. CF 3 SB CAM FOLLOWER BEARING ; 3" RLR DIA 1-3/4" RLR WD Buy online from BDI – Bearing ...
2, F7 for housings made from flake graphite cast iron GG, if bearing outside diameter D ï¼ 250 mm and temperature difference between outer ring and housing ï¼ 10 K.
Gently slide the wheel hub assembly off the spindle. At this point, you may need to tap the back of the hub with a hammer to loosen it. Once removed, the old wheel bearings should be visible.
Bearingodtolerancechart
Home Engineering Book Store Engineering Forum Applications and Design Beam Deflections and Stress Bearing Apps, Specs & Data Belt Design Data Calcs Civil Engineering Design & Manufacturability Electric Motor Alternators Engineering Calculators Excel App. Downloads Flat Plate Stress Calcs Fluids Flow Engineering Friction Engineering Gears Design Engineering General Design Engineering Hardware, Imperial, Inch Hardware, Metric, ISO Heat Transfer Hydraulics Pneumatics HVAC Systems Calcs Economics Engineering Electronics Instrumentation Engineering Mathematics Engineering Standards Finishing and Plating Friction Formulas Apps Lubrication Data Apps Machine Design Apps Manufacturing Processes Materials and Specifications Mechanical Tolerances Specs Plastics Synthetics Power Transmission Tech. Pressure Vessel Pumps Applications Re-Bar Shapes Apps Section Properties Apps Strength of Materials Spring Design Apps Structural Shapes Threads & Torque Calcs Thermodynamics Physics Vibration Engineering Videos Design Manufacture Volume of Solids Calculators Welding Stress Calculations Training Online Engineering
Bearing tolerancestandard
This is mitivac's music collection on Bandcamp. Start your own! edit profile. Follow. Following. Unfollow. mitivac. Italy; Classical.
Slide the wheel hub assembly back onto the spindle, making sure it aligns properly. Reinstall the castle nut and tighten it to the manufacturer's specified torque using a socket and torque wrench. Insert a new cotter pin through the spindle and castle nut, bending the ends to secure it. Replace the dust cap or grease cap, ensuring it is seated snugly.
Bearing Engineering and Knowledge Application Menu Tolerances, Engineering Design & Limits & Fits Bearing Shaft and Housing Installation Tolerances Size and fit tolerances for bearing mating shafts and housing are provided within the tables below are defined by ISO tolerances for shafts and housings (ISO 286) in conjunction with the tolerances Îdmp for the bore and ÎDmp for the outside diameter of the bearings per. (DIN 620). The tables provided are design recommendation and should not supercede ABEC, ISO or OEM recommended fits and tolerances. Tolerance zones amd variability The ISO tolerances are defined in the form of tolerance zones. They are determined by their position relative to the zero line (= tolerance position) and their size (= tolerance grade, see ISO 286). The tolerance position is indicated by letters (upper case for housings, lower case for shafts). For a schematic representation of the most common rolling bearing fits. The tables as below contain recommendations for the selection of shaft and housing tolerances that are valid for normal fitting and operating conditions. Tolerance specification deviations are possible if particular requirements apply, for example in relation to running accuracy, smooth running or operating temperature. Increased running accuracies thus require closer tolerances such as tolerance grade 5 instead of 6. If the inner ring is warmer than the shaft during operation, the seating may loosen to an impermissible extent. A tighter fit must then be selected, for example m6 instead of k6. In such cases, the question of fits can only be resolved by a compromise. The individual requirements must be weighed against each other and those fulfilled that give the best overall solution. Related: Preferred Tolerances Metric ISO 286 Table of Hole Bore Tolerances per. ISO 286 Calculator Table of Shaft Tolerances per. ISO 286 Calculator Roller Bearing Fits and Tolerances Designations (Click on image to enlarge) Zero line (Line-to-Line Fit) Nominal diameter Loose fit Transition fit Tight fit Shaft diameter Housing bore ÎDmp = tolerance for bearing outside diameter Îdmp = tolerance for bearing bore Shaft tolerances for radial bearings with cylindrical bore Condition of rotation Bearing type Shaft diameter mm Displacement facility Load Tolerance zone Point load on inner ring Ball bearings, roller bearings All sizes Inner ring easily displaced g6 (g5) Inner ring not easily displaced, angular contact ball bearings and tapered roller bearings with adjusted inner ring h6 (j6) Needle roller bearings All sizes Non-locating bearing h6 (g6)1) Circumferential load on inner ring or indeterminate load direction Ball bearings up to 50 Normal loads2 j6 (j5) 50 to 100 Low loads3 j6 (j5) Normal and high loads4) k6 (k5) 100 to 200 Low loads2 k6 (m6) Normal and high loads5 m6 (m5) over 200 Low loads m6 (m5) Normal and high loads n6 (n5) Roller bearings up to 60 Low loads j6 (j5) Normal and high loads k6 (k5) 60 to 200 Low loads k6 (k5) Normal loads m6 (m5) High loads n6 (n5) 200 to 500 Normal loads m6 (n6) High loads, shocks p6 over 500 Normal loads n6 (p6) High loads p6 Needle roller bearings up to 50 Low loads k6 Normal and high loads m6 50 to 120 Low loads m6 Normal and high loads n6 120 to 250 Low loads n6 Normal and high loads p6 250 to 400 Low loads p6 Normal and high loads r6 400 to 500 Low loads r6 Normal and high loads s6 over 500 Low loads r6 Normal and high loads s6 For easier fitting. C/P ï¼ 10 C/P ï¼ 12 C/P ï¼ 12 C/P ï¼ 10 Shaft tolerances for axial bearings Load Bearing type Shaft diameter Operating conditions Tolerance zone Axial load Axial deep groove ball bearings All sizes - j6 Axial deep groove ball bearings, double direction - k6 Axial cylindrical roller bearings with shaft locating washer - h6 (j6) Axial cylindrical roller and cage assemblies - h8 Combined load Axial spherical roller bearings All sizes Point load on shaft locating washer j6 up to 200 mm Circumferential load on shaft locating washer j6 (k6) over 200 mm k6 (m6) Housing tolerances radial bearings Condition of rotation Displacement facility Load Operating conditions Tolerance zone Point load on outer ring Outer ring easily displaced, housing un split The tolerance grade is determined by the running accuracy required H7 (H6)1) Outer ring easily displaced, housing split H8 (H7) Outer ring not easily displaced, housing un split High running accuracy required H6 (J6) Outer ring not easily displaced, angular contact ball bearings and tapered roller bearings with adjusted outer ring Housing split Normal running accuracy H7 (J7) Outer ring easily displaced Heat input via shaft G72) Circumferential load on outer ring or indeterminate load direction Low loads, outer ring cannot be displaced For high running accuracy requirements: K6, M6, N6 and P6 K7 (K6) Normal loads, shocks, outer ring cannot be displaced M7 (M6) High loads, shocks (C/P ï¼ 6), outer ring cannot be displaced N7 (N6) High loads, severe shocks, thin-walled housing, outer ring cannot be displaced P7 (P6) 1, G7 for housings made from flake graphite cast iron GG, if bearing outside diameter D ï¼ 250 mm and temperature difference between outer ring and housing ï¼ 10 K. 2, F7 for housings made from flake graphite cast iron GG, if bearing outside diameter D ï¼ 250 mm and temperature difference between outer ring and housing ï¼ 10 K. Housing tolerances for axial bearings Load Bearing type Operating conditions Tolerance zone Axial load Axial deep groove ball bearings Normal running accuracy High running accuracy E8 H6 Axial cylindrical roller bearings with housing locating washer - H7 (K7) Axial cylindrical roller and cage assemblies - H10 Axial spherical roller bearings Normal loads High loads E8 G7 Combined loads Point load on housing locating washer Axial spherical roller bearings - H7 Combined loads Circumferential load on housing locating washer Axial spherical roller bearings - K7 Source ISO 286 DIN 620 Related Shaft to Shaft Axial Alignment Design Tolerances Tables Housing Tolerance Classifications for Metric Radial Ball and Roller Bearings Shaft Tolerance Radial Ball and Roller Bearings GD&T Application Single Datum Axis - Two Datum Features General ISO Geometrical Tolerances Per. ISO 2768 Ball Bearings ABEC Standard Tolerances Data Bearing Types and Application Design | Ball Bearings | Roller Bearings | Thrust Bearings
UV-25 Walkie Talkie Powerful 10W Portable Ham Radios FM Wireless Two-Way Radios. ☆K-portCompatible with K-port (2 Pin) headset, speaker mic, ...
Safety should always be a priority, so be sure to follow all safety precautions, wear appropriate protective gear, and work in a well-ventilated location.
The most common symptom of bad wheel bearings is a grinding or roaring sound coming from the wheels. Other signs include vibrations in the steering wheel, uneven tire wear, and difficulty turning the wheels. If you experience any of these issues, have your car inspected by a qualified mechanic.
Most industrial facilities have bearings that rotate faster than normal processing equipment. When it comes to lubricating these pieces of equipment, ...
In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk you through the step-by-step process of replacing your car's wheel bearings, enabling you to revamp your ride and regain that smooth, worry-free driving experience.
Size and fit tolerances for bearing mating shafts and housing are provided within the tables below are defined by ISO tolerances for shafts and housings (ISO 286) in conjunction with the tolerances Îdmp for the bore and ÎDmp for the outside diameter of the bearings per. (DIN 620).
If you removed the brake rotor, carefully place it back onto the wheel hub. Secure it with any retaining screws or bolts. Reattach the brake caliper to its original position, tightening the bolts or pins according to the manufacturer's specifications.
Before you embark on this DIY journey, it's important to note that working on your own wheel bearings requires a moderate level of mechanical knowledge and experience. If you feel unsure at any point, it's best to consult a professional mechanic, such as those at Goodhood mobile auto repair services.
Locate the wheel hub assembly, which houses the wheel bearings. It is typically located behind the brake rotor. Remove the brake caliper by loosening the bolts or pins and securing it. Hang the caliper using a wire or bungee cord to prevent putting strain on the brake line. If necessary, detach the brake rotor by removing any retaining screws or bolts
Over time, these bearings wear out and compromise the performance of your vehicle. While it's always recommended to seek professional assistance for complex repairs, wheel bearing replacement is a task that can be tackled by experienced DIY enthusiasts.
Maintaining your own vehicle is an essential part of being a responsible car owner. Regular inspections and timely repairs can keep your ride running smoothly and ensure your safety on the road. One critical component that requires attention is the wheel bearings.
Thoroughly clean the wheel hub and spindle using a degreaser and a clean rag. Inspect the spindle for any signs of damage or wear. Additionally, examine the wheel hub for cracks, excessive play, or pitting. If any significant issues are detected, it may be necessary to replace the entire hub assembly.
An authority may commence an eminent domain proceeding or designate the property to be exempt from eminent domain under the plan at any time before the ...
Driving with bad wheel bearings can be dangerous. It increases the risk of a serious accident and puts you in danger, so it's best to avoid driving if you suspect your wheel bearings need to be replaced. Have a qualified mechanic inspect the vehicle as soon as possible and replace any worn-out parts.
The front wheel bearings require a bit more work. Pull out the cotter pin that secures the axle spindle nut and remove it. Pry off the outer wheel bearing race using a screwdriver. Pull out the inner wheel bearing with a hammer, being careful not to damage the spindle or other parts of the wheel hub assembly.




 8613869596835
8613869596835