Quick Tip: How to Check and Add Grease to Trailer Wheel ... - best boat trailer bearing grease
The patients’ pulmonary function variables were expressed in relation to the amount predicted for healthy subjects with similar age, weight, and height. In order to examine the hypothetical relationship between FEF25-75 and AHR, the subjects were subdivided into 3 groups according to the baseline FEF25-75%: FEF25-75≤50% or FEF25-75>50 and ≤65% or FEF25-75>65%.
I'm looking for a turntable, that's it-- like a bar stool that spins 'round. a lazy susan bearing. Only, I want it to either click into place at ...
6203Zbearing dimensions
Mean FEF25-75 value was 70.9 ± 19.2 and 84.2 ± 22.7, for patients with positive and negative Methacholine challenge test result, respectively, and the difference was statistically significant (t = 4.003, p-value<0.001). In other words, mean FEF25-75 value is lower for patients with hyper-responsiveness airways.
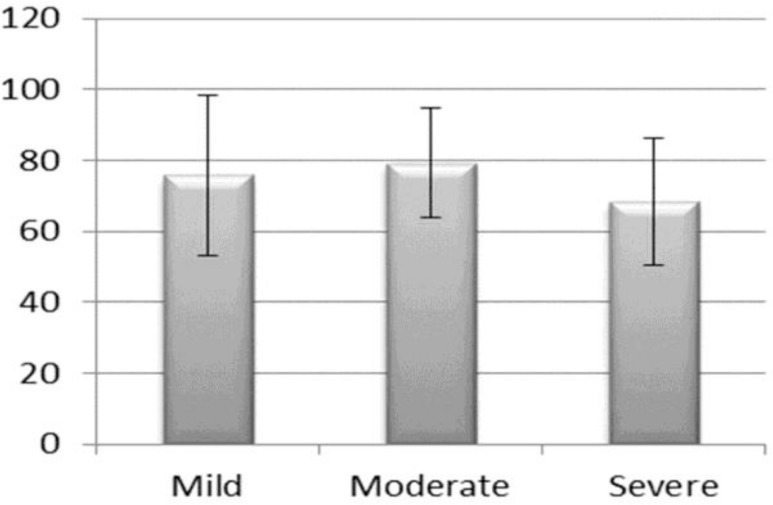
Later on all positive methacholine test subjects were subdivided in groups on the basis of bronchial hyper-responsiveness (≤ 1000 μg, between 1001–2000 μg; and ≥ 2001 μg), one-way ANOVA results indicated that mean FEF25-75 value was significantly lower for severe bronchial hyper-responsiveness group (F=3.78, df=3, P-value = 0.025; Figure-1).
Currie et al. (17) evaluated asthmatic patients with borderline methacholine challenge test. They measured the patients’ AHR and showed that the rate of FEF25-75 in patients with moderate-to-severe AHR was significantly lower, suggesting FEF25-75 as a marker of asthma severity. The results of the present study are not consistent with those of other studies in which lower rates of FEF25-75 have an inverse relationship with airway AHR. In fact, in this study no relationship was observed between FEF25-75 and AHR, and higher impairment of FEF25-75 did not correspond to a more severe AHR.
The tests were conducted at the Pulmonary Department of Imam Khomeini Hospital. Methacholine solutions were prepared using dry methacholine powder based on aseptic technique by trained personnel. A methacholine concentration of 0.06 mg/ml to 16 mg/ml was diluted in normal saline (0.9% sodium chloride). The patients received the solutions via an Aerosol-Dosimeter ProvoJet (Ganshorn Medizin Electronic).
In conclusion, patients with asthma symptoms and “normal” FEV1, FVC and FEV1/FVC, but impaired FEF25-75, are recommended to perform a bronchoprovocation test. Unfortunately, a significant cut-off of FEF25-75 could not be found to help find the distinction between hyper-reactive and normo-reactive airway in that FEF25-75 can be low in normo-reactive subjects. In addition, no association was found between a greater impairment of FEF25-75 and a more severe AHR.
6203ZBearing Price
We did not find a major FEF25-75 cut-off value to distinguish hyper-reactive from normo-reactive subjects. This means that FEF25-75 can only be considered an AHR risk factor and could not differentiate hyper-reactive from normo-reactive subjects.
We speculate that along with normal FEV1, FEF25-75 may also be clinically worthwhile in diagnosis of asthmatic patients with undesirable asthma outcomes. Further, for the majority of asthmatic patients who have a normal FEV1, other findings of spirometry measurement are associated with poor asthma outcomes, and these have important implications for clinicians and investigators looking for a suitable asthma outcome measurement (13,14).
Our special thanks go to all patients who participated in this study. This work was funded by Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences (Grant Number: DU-9302; Code of ethics: IR.AJUMS.REC.1393.167). Hereby, we acknowledge the deputy vice-chancellor for research and technology affairs of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences.
6203ZBearing near me
In addition, frequency distribution of hyper-responsiveness had an interesting pattern. The group with severe hyper-responsiveness had the highest frequency, as illustrated in table 2. However, among patients with mild, moderate and severe AHR, there was no significant difference when going from baseline values of FEF25-75<50% to values >65% with the increase of baseline FEF25-75%. In addition, no change in the median PD20 was observed among patients whose baseline FEF25-75% was higher.
The size of a bearing is typically measured by its inner diameter (ID), outer diameter (OD), and width (W), and listed in the format "ID x OD x W."
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
In the present study, similar to study of Sposato et al. (18), there was a drop in FEF25-75 rate among patients with normal reactivity. Therefore, small airway impairment measured by a decrease in FEF25-75 could be considered as a useful approach to detect impairment associated with other asthma parameters such as typical symptoms, wheezing, and atopy. Reduction of FEF25-75 in normo-reactive subjects or hyper-reactivity apart from asthma, may be due to air pollution, occupational exposure, smoking, early stage of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) and other factors that are still unknown.
Bronchial hyper-responsiveness is defined as an abnormal bronchial response to stimulants and it has been considered as a typical characteristic of chronic asthma (1). One of the most important parameters for the diagnosis and post-diagnosis follow-up of asthma is the Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second (FEV1). However, recent studies have demonstrated that asthmatic patients with a normal FEV1 may have ventilatory defects (2) and suggest another parameter which is the expiratory flow between 25% and 75% of vital capacity (FEF25-75) which is more reflective of small airways and a sensitive indicator of symptomatic asthma, compared to FEV1, in detecting airways limitation (2–4). What distinguishes FEF25-75 from FEV1 is the fact that the recorded values in the latter are concerned with the whole bronchial tree, while the former provides values specifically related to the bronchial zone between division 7 and division 19, the internal diameter of which is between 0.5 and 2 mm. In addition, whereas the values of FEV1 are more reliable in showing the degree of bronchial obstruction, FEF25-75 is more variable and sometimes used when FEV1 is within normal limits (5,6). Since small airways are more susceptible to inflammatory and remodeling processes, it is important to determine whether FEF25-75 is a preferred tool in assessing AHR when the methacholine challenge test is performed (7,8). The combination of a low FEF25-75 and a normal FEV1 as a hallmark of asthma is not yet well established (4). No guidelines have been offered as to find normal FEF25-75 values. In this regard, a FEF25-75 cut-off value has recently been proposed for a group of asthmatic children: FEF25-75 less than 65% of predicted is considered impaired (3). Impaired FEF25-75 may be suggestive of severe bronchial hyper-reactivity in patients with recent onset of allergic rhinitis. A positive response to bronchodilator and an underlying bronchial inflammation can be assessed by Fractional exhaled Nitric oxide (FeNO) measurement (9). The Methacholine Challenge Test (MCT) has been used universally to assess bronchial hyper-responsiveness in patients with asthma. Although MCT is as a standard method to confirm the presence of airway hyper-responsiveness, it has its own limitations (in available and cost of procedure) that restrict its use as a tool for definitive diagnosis of asthma (10). Consecutive methacholine doses are administered until FEV1 is seen to decrease by 20 percent (PD20) (11).
Subjects were divided into three groups based on the extent of methacholine required to attain the aforesaid parameters: Group 1 (Severe):≤1000μg; Group 2 (Moderate): 1001–2000μg; and Group 3 (Mild):≥2001μg (11). They were also classified according to FEF25-75 into three groups: FEF<50, 50<65 and FEF>65.
6203ZBearing
The current study was designed to assess the presence of Airway Hyper-responsiveness (AHR) in a large group of adults suffering from an acute rainfall dyspnoea, to examine the relationship between FEF25-75 and methacholine airway responsiveness, to confirm a cut-off value for FEF25-75 in these patients and determine a relationship between baseline FEF25-75 and AHR. More specifically, the relationship between a greater impairment of FEF25-75 and a more severe AHR was aimed to be investigated.
A study performed in this respect on children with a low FEF25-75 and normal FEV1 showed low FEF25-75 was significantly associated with asthma intensification and severity and the application of steroids (4). The finding of another study confirmed that small airway dysfunction is associated with a more severe AHR, nocturnal asthma, more exacerbations, asthma induced by exercise, poor asthma control and late-phase allergic response (15). These results suggest the possible role of FEF25-75 as a marker of asthma severity particularly in patients with normal FEV1 and FEV1/FVC. Also, low rates of FEF25-75 were negatively related to FeNO value (16) suggesting that in the initial phases of the disease, distal airways as opposed to proximal ones are subject to more severe inflammation and airflow obstruction. Therefore, FEF25-75 rather than FEV1 and FEV1/FVC is a better marker in this regard. In these patients, methacholine challenge test can confirm an asthma diagnosis.
Frequency of people getting either a negative or positive methacholine test was significantly different for different groups based on their FEF25-75 values (p-value=0.01) (Table 1). When we subdivided all patients in groups according to the baseline FEF25-75 values (<50%, between 50 and 65% and >65%), the values of positive methacholine test decreased significantly when going from FEF25-75<50% to values >65% (Table 1). Also these percentages for negative tests were converse.
Goldwagen proudly carries a large number of line items for a wide variety of popular vehicle brands, including Audi, BMW, Chevrolet, Ford, Hyundai, Jeep, ...
2015419 — I would say with a roller bearing like the one you have shown, that the bevel end (not the flat end), should be installed out to receive the 4sp input shaft.
VA-120. Image for Illustration purposes only. Actual product may vary. Harwal VA120 VA-120 NBR V-Ring. MODEL VA-120. BRAND. Harwal. SKU. 2395643. UOM. each.
Year, Make, Model, Submodel, Engine, Attributes. 2018, Ford, F-150, Raptor, 6 Cyl 3.5L, Crew Cab Pickup. 2018, Ford, F-150, Raptor ...
Ntn6203ZBearing
When asthma begins, AHR could be predicted by impaired FEF25-75 with normal FEV1 and FEV1/FVC. However, we could not determine a cut-off value, and no association was found between a greater impairment of FEF25-75 and a more severe AHR.
Timken’s deep groove ball bearings deliver reliable performance in a wide range of applications and conditions. With super-finished raceways and controlled geometries, our premium design helps ensure consistent quality.
In a cross sectional study in Imam Khomeini Hospital, Ahvaz, patients suffering from respiratory symptoms due the 2013 autumn rainfall with normal FEV1 and FEV1/FVC were evaluated by methacholine challenge test. Those with PD20<1000, 1000<2000 or >2000 μg were classified as severe, moderate and mild AHR, respectively. Data were analyzed using Chi-square, Independent t-test, One-way ANOVA and Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve.
134-7448, Timken, Timken L44643/L44610 25.4mm I.D Taper Roller Bearing, 50.29mm O.D, Brand Timken, Inside Diameter 25.4mm, Outside Diameter 50.29mm, ...
Bearing6203ZSpecification
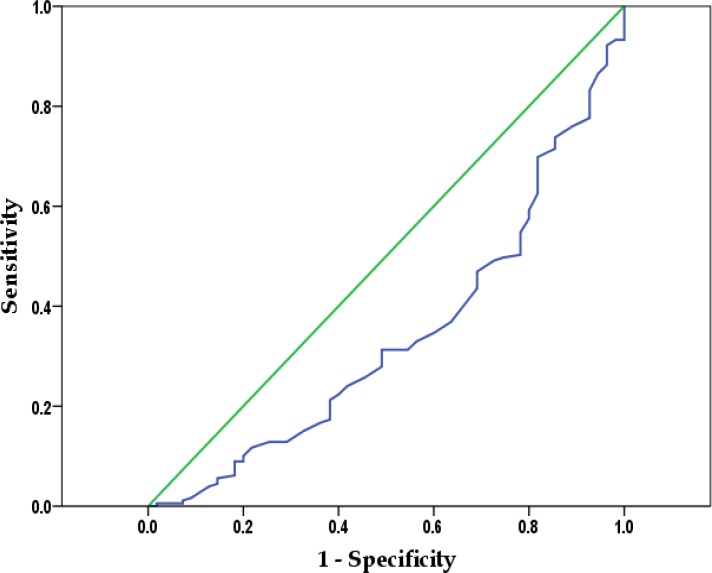
Among the 234 patients, mean baseline FEF25-75 was 84.2±22.7% for 54 patients having a negative bronchial provocation test result and 70.9±19.2% for 179 patients with a positive bronchial provocation test result (P < 0.0001). No change was observed in the median PD20 among patients with a higher baseline FEF25-75. ROC analysis showed that FEF25-75 could potentially be a predictor of AHR, but it could not confirm the cut-off value of FEF25-75 for these patients.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
(PRESTIGE)(SGA-050)「にまたがりらをりす8」りょう33?r し. weimeizhiyu. . Rank: 6. : 1521; : 47578. ...
Correspondence to: Borsi SH, Address: Air pollution and Respiratory Diseases Research Center, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran, Email address: Seyedhamidborsi@yahoo.com
The present study, carried out on patients with asthma like symptoms and normal pulmonary function, highlights that a drop in baseline FEF25-75 is associated with a rise in the number of hyper responsive patients but does not correspond with levels of AHR. Furthermore, we can only say that a smaller rate of FEF25-75 denotes an AHR risk factor.
A Receiver-Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was conducted to evaluate the ability of FEF25-75% to predict airway AHR. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis specificity was performed using SPSS version 22.0.
6204 bearing Dimensions
View 67 photos for 11801 1st St E, Treasure Island, FL 33706, a 3 bed, 3 bath, 2226 Sq. Ft. townhomes home built in 2023 that was last sold on 04/01/2024.
Shop Hydraulic Seal Distributors ; SKF Rotary Shaft Seal: 1 Lip, HM1, … $22.53 ; Dds Rotary Shaft Seal: 1 Lip W/Spr… $10.11 ; SKF Rotary Shaft Seal: 1 Lip W/Spr…
All participants underwent basal spirometry. The patients’ pulmonary function report involved their age, gender, weight, height, and smoking status. Abiding by ATS/ERS guidelines (8) regarding the standards of lung function testing, spirometric assessment was conducted using a spirometer (Ganshorn medizin electronic) and the best test is defined as the best FVC, FEV1 and FEF25-75 of all the reproducible tests; these data also were used to calculate FEV1/FVC ratio.
The aim of the present study was threefold: to assess the association between baseline FEF25-75 and Airway Hyper-responsiveness (AHR), to specify whether a decrease in FEF25-75 may reflect severe hyper-responsiveness, and finally to confirm a FEF 25-75 cut-off value.
After baseline spirometry, methacholine was inhaled according to ATS guidelines where a 2-min tidal breathing method was used with a synchronized nebulizer (12). Nebulized methacholine was inhaled for 2 minutes, and there were 5-minute intervals between doses. Seven inhalations of increasing concentrations of methacholine were administered, namely 0.06, 0.125, 0.5, 1, 4, 8 and 16 mg/ml, until the highest concentration (16 mg/ml) or the end-point (a 20% decrease in FEV1) was reached. Spirometry was performed 3 minutes after each increasing dose of methacholine. Patients in whom a 20% fall in FEV1 with a methacholine dose of 16 mg/ml was not observed, were considered normal.
The present study was a cross-sectional study carried out at the Department of Pulmonology, Imam Khomeini Hospital, Ahvaz, Iran. It was approved by Ahvaz University of Medical Sciences with DU-9302 number. In this study, 236 adults with asthma-like symptoms due to the 2013 autumn rainfall and with normal FEV1 and FEV1 / FVC were evaluated by performing the methacholine challenge test. In fact, since all patients had asthma-like symptoms (e.g., inexplicable acute attacks of cough, wheezing, dyspnea, etc.) due to rainfall with a normal spirometry, they were subject to a methacholine challenge test. The use of spirometer and methacholine challenge test data was approved by the Ethics Committee of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences.
Of the 236 patients with asthma-like symptoms, 113 (47.9 %) were male and 123 (52.1 %) were female. Average age of the subjects was 28.4 ± 12.3 years (range: 23–64). About 13.7% of the patients were smokers. Pervious history of asthma was positive in 26.1%. Methacholine challenge test results were positive for 182 (77.1%) subjects and negative for 54 (22.9%).
NSK6203ZBearing
In order to determine optimal discrimination threshold values for FEF25-75, ROC curve was used, but a cut-off point for bronchial hyper-responsive could not be determined (Figure 2).
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
The study limitation was the absence of long term follow up of patients for evaluating and comparing the number of asthma exacerbations and patients’ outcome.
The patients with normal respiratory function with FEV1/FVC > 70% were included. Exclusion criteria contained failure to perform spirometry with an acceptable quality, history of heart attack or stroke within the last 3 months, uncontrolled hypertension (systolic BP > 200 mmHg, or diastolic BP > 100 mmHg), current use of corticosteroid, beta agonist, anticholinergic, theophylline, antileukotriene, chromones, beta-blocker and cholinesterase inhibitor medication (for myasthenia gravis), pregnancy, and unwillingness to participate. A standard questionnaire was used to record demographic details such as age, sex, spirometry and methacholine test results. All participants signed a written informed consent.
Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was employed to determine whether sample data were normally distributed (p.value>0.05). Data analysis was performed using descriptive statistics such as frequency, frequency percentage, mean and standard deviation. Statistical inferences were made based on different tests including independent t-test, Chi-square, and one-way ANOVA.




 8613869596835
8613869596835