Replace wheel bearing or entire hub assembly? - how to replace hub bearings
Under normal driving conditions, wheel bearings should last 85,000 to 100,000 miles. They can fail for several reasons, including:
Frontwheel bearingreplacementcost
Ignoring tolerance will add to challenges in assembly and increase cost significantly. Here are our ideas if you need to reduce these challenges.
The standard ISO 286 defines the system of tolerances, deviations, and fits only for basic sizes up to 3150 mm. However, IT grades can be extrapolated in the following way.
International Standard ISO 2768:1989 was prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC3, Limits, and fits, it comes in two parts, namely ISO 2768-1 and ISO 2768-2.
Wheel bearingreplacementcostNear Me
On modern front- and four-wheel-drive cars, wheel bearings are a set of permanently sealed, precisely machined steel ball or straight roller bearings. The balls or rollers are encased in a “cage” that supports the bearings, allowing them to rotate freely.
Approximate dimensions are used when the tolerances are not very important. They are indicated by using the term “APPROX.” before or after the dimensional value. They are often indicated using “ca.” or “~”. There is no supervision or measurement of approximate dimensions. For example, 10.5 APPROX. could be any value close to 10.5mm.
NOTE: Whether you DIY or your mechanic replaces the bearing, always install a new axle hub nut. Most hub nuts are prevailing torque fasteners. They’re used on critical components, like securing axle shafts to hub bearings, where a loose nut could lead to disastrous consequences.
Frontwheel bearingreplacementcostNear me
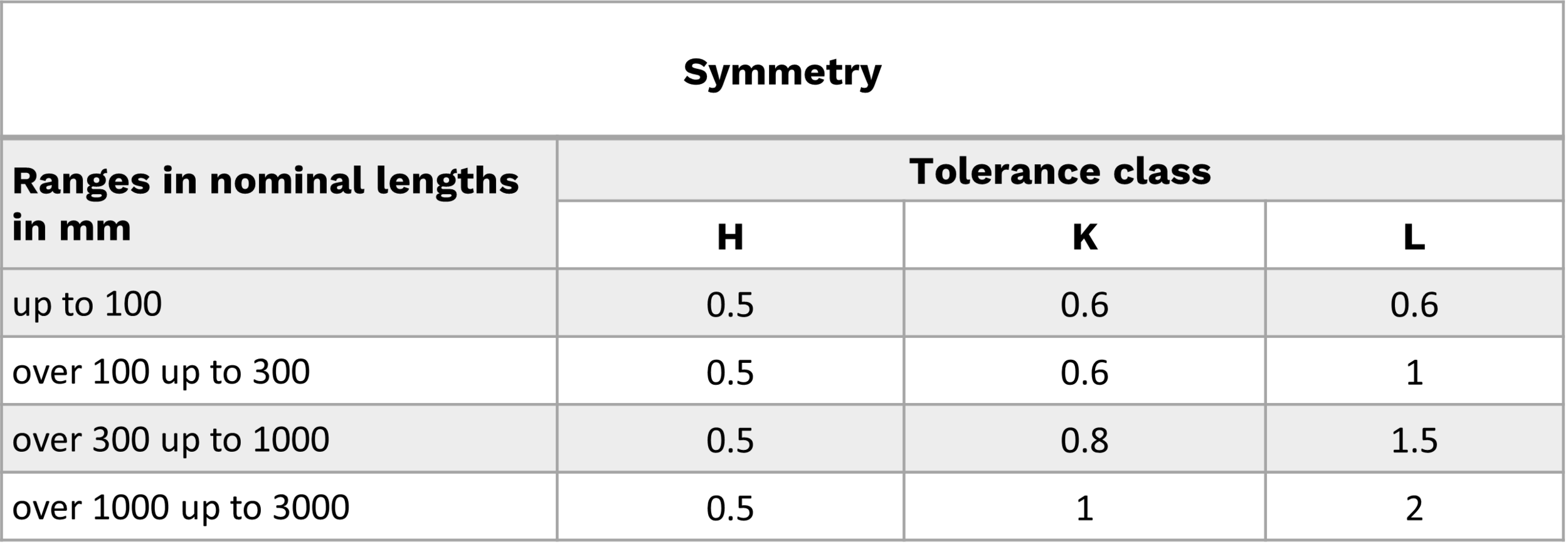
Theoretically Exact Dimensions (TED) or Theoretically Exact Measures (TEM), are also called Basic Dimensions. TED are given from a datum to a feature of interest. TED are defined as a numerical value to describe the theoretically exact size, profile, or location of a feature. Variations allowed to these dimensions are based on feature controls, notes, or tolerance of other dimensions. No tolerance is specified explicitly to TED.
We are no longer supporting IE (Internet Explorer) as we strive to provide site experiences for browsers that support new web standards and security practices.
Jiffy Lubewheel bearingreplacementcost
Driving on a bad or failing wheel bearing is dangerous. If ignored, it can quickly turn into a safety issue and an expensive repair.
Tolerances are generally controlled by ISO 2768 standard. ISO 2768 tolerancing is based on the size of the feature. Small feature sizes have closer tolerances and large features feature sizes have larger tolerances.
Rearwheel bearingreplacementcost
The system considers both the nominal size as well as the tolerance width to determine a proxy for the “manufacturing complexity”
The upper limit is the largest the feature can be within the given tolerance of the dimension. The lower limit is the smallest the feature can be within the given tolerance of the dimension.
The average cost to replace a sealed wheel hub bearing is around $350 per wheel. However, depending on the make and model, the shop labor rate ($47 to $215 per hour, according to AAA) and any additional damage could push the cost beyond $1,000 per wheel.
However, on some vehicles, it can be less than $100 per wheel. And you can save hundreds in labor if you DIY. If you don’t have the tools, most auto parts stores will lend you the specialty tools and equipment needed.
How much does it cost for a new wheel bearingnear me
Limit tolerance is an alternative method of showing and calculating tolerance. With limit dimensioning, the extreme values of the tolerance are given in the dimension. The limits are upper limit and the lower limit.
The relation between two mating parts due to the difference between their sizes before the assembly, is defined as fits.
From IT6 to IT18, the standard tolerances are multiplied by the factor 10 at each fifth step. This rule applies to all standard tolerances and may be used to extrapolate values for IT grades not given in Table 1. For example, the nominal size range 180 mm up to and including 250 mm, the value of IT20 is:
IT grades do not specify how the tolerance limits are distributed around the nominal value, IT grades with an alternate prefix are used for this purpose. For example, the prefix ‘js’ is used in place of ‘IT’ to specify the symmetrical distribution, so a dimension 12 js5 is equivalent to 12±0.004 (where 12 IT7 is 0.008).
A bilateral tolerance is allowed to vary in two directions from the specified dimension. For example, 10.5(+0.2/-0.1) is an unequal bilateral tolerance and the dimension 10.5±0.2 is called an equal bilateral tolerance.
Deviation is plus-minus dimensioning. It uses a bilateral or unilateral tolerance format, depending on the application. Plus-minus dimension values are placed using the plus-minus symbol (±). For example, 10.5±0.2 or 0.250±0.005.
Tolerance defines the acceptable range of variation allowed on a dimension. It helps to define criticality in the part and ensure assembly.
A unilateral tolerance varies in only one direction from the specified dimension. For example, 10.5 +0.2/-0 or 10.5 +0/-0.1.
IT grade(s) describe an internationally accepted code system that categorizes the linear tolerances into 12 categories. This allows Product Owners and Data Scientists to handle tolerances with a single number. The system is defined in ISO 286 and frequently used.
In my 50 years in the auto repair industry, I can’t recall one good story about wheel bearings. Most involve some sort of brake system failure, tires exploding, or fire from a seized red-hot bearing igniting axle grease. Bad wheel bearings should not be ignored.
Wheel bearingreplacement near me
Wheel Bearing costAutoZone
Wheel bearings allow cars and trucks to run smoother and more efficiently by reducing friction and supporting vehicle weight.
The ISO 2768 only applies to the following drawings with the subsequent features. It is used when these functions do not have custom tolerance indications individually:
Reference dimensions are used to provide information or visualization only. Reference dimensions are often used as additional information to accumulation of other dimensions or to show a dimension that is defined elsewhere with tolerance. No tolerance is defined explicitly for a reference dimension and no inspection is necessary.
Never reuse any wheel bearing (sealed or tapered) that’s loose, worn, noisy or shows any signs of wear. Trying to fix a loose or damaged wheel bearing can result in an accident and severe injury. Even if a pro suggests repairing a bearing, don’t let them.
Older rear-wheel-drive cars or trailers use a set of two tapered roller bearings that face each other. These should be routinely serviced every 20,000 miles, or once a year.
My opinion? If your vehicle has more than 50,000 miles or has been driven in harsh conditions, then it’s logical to replacing wheel bearings on both axles. However, if your vehicle has low mileage and the other bearing is in good condition, replacing only the damaged bearing should not be a problem.
There are four classes of size tolerances: fine(f), medium(m), coarse(c) and very coarse(v). For example, a company that manufactures precision parts and equipments might select the medium(m) for general metric tolerances. This is given by ISO 2768-m, the tolerances for various dimensions will be given by the general metric tolerance table.
I’ve replaced hundreds, if not thousands, of wheel bearings. One thing I’ve learned: A bad wheel bearing always gives an indication it’s failing. These include:
Various features such as chamfers, fillets, rounds, hole depths, and thread lengths, can be dimensioned with single limits. The abbreviation for minimum (MIN) or maximum (MAX) follows the dimension value to specify a single limit application. The unspecified limit is 0 when MAX is used or reaches infinity when MIN is specified. For example, R6MIN means the minimum radius should be 6mm or RMAX6 means the maximum radius can be 6mm.
Reference dimensions are defined by using parenthesis around the dimension or using the term “REF” or “Ref.” behind the dimension. For example, (10.5) or 10.5 REF or 10.5 Ref.
The cage and rollers are held together inside a hardened metal ring called a “race.” The seal keeps grease in and damaging water and debris out. Wheel bearings are installed inside, and secured to, the suspension, either by press-fit, bolts or a snap-ring. Once mounted, the wheel bearing rides on the axle shaft, allowing the tire/wheel to spin effortlessly.
Theoretically Exact Dimensions are used to prevent accumulation of tolerance. Chain dimensioning using Tolerance-based Dimensions can cause accumulation of tolerance as the tolerances of all chain dimensions would add up.
For example, here the tolerances of dimension 25, 10 and 15 will add up to define position of the ø10 hole, resulting in a higher tolerance band. This can be avoided using theoretically exact dimensions.
Standardized prefixes include the letters A, B, C, CD, D, E, EF, F, G, H, J, JS, K, M, N, P, R, S, T, U, V, X, Y, Z, ZA, ZB, ZC (for holes), and the lower-case equivalents (for shafts). All of these letters represent some kind of distribution around the nominal value. H and h are easiest to explain as the tolerance lies entirely on one side of the nominal size.




 8613869596835
8613869596835