Symptoms of Bad Wheel Bearings - how long can you drive with a bad wheel bearing
Axial vs radialmeasurement
Radial load refers to a force that acts perpendicular to the axis of an object. Unlike axial load, which acts parallel to the axis, radial load applies a force that is perpendicular or tangential to the axis.
In summary, axial loads have widespread applications in civil engineering, mechanical engineering, aerospace, and automotive industries. Understanding and accurately assessing these loads are vital for the proper design and functionality of various structures and components.
In power generation facilities, radial loads are present in turbines, generators, and other rotating equipment. These loads can impact the efficiency, stability, and reliability of the power generation process.
In the construction of buildings and bridges, axial loads play a vital role in determining the strength and stability of structural members. Columns, beams, and walls are designed to withstand the axial loads resulting from the weight of the structure itself, as well as the loads imposed by occupants, furniture, and environmental factors.
So, the next time you encounter axial load or radial load in your engineering endeavors, remember the importance of considering these forces and their implications. Armed with this knowledge, you can make informed decisions, solve problems, and contribute to the advancement of your field.
Aug 27, 2017 — If the knock is a single loud knock everytime the engine turns 360 degrees, rod bearing. If the knock is more of a quick double knock, possible ...
We and selected third parties use cookies (or similar technologies) for technical purposes, to enhance and analyze site usage, to support our marketing efforts, and for other purposes described in our Cookie Policy
We will explore the definitions, examples, and applications of axial and radial loads, helping you gain a deep understanding of their significance. By the end of this article, you will be equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions and solve problems related to axial and radial loads.
Axial loadexample
In the automotive industry, radial loads are encountered in various components, such as wheel bearings, engine crankshafts, and transmission systems. Proper design and analysis of these components are crucial for ensuring optimal performance, durability, and safety on the road.
13931 is an odd five-digits prime number following 13930 and preceding 13932. In scientific notation, it is written as 1.3931 × 104. The sum of its digits is 17 ...
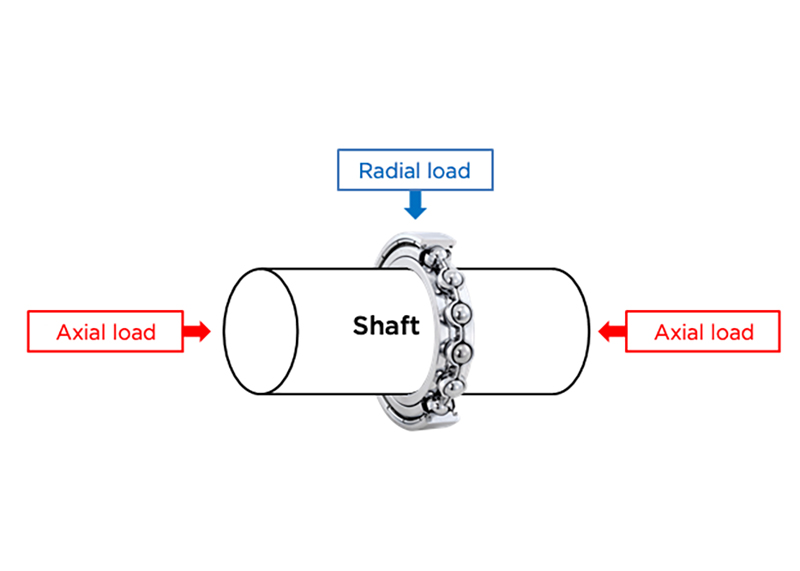
Radial loadbearing
By accurately assessing the magnitude and direction of axial and radial loads, engineers can optimize the design, material selection, and reinforcement of structures and components. This optimization leads to cost-effective solutions, reduced maintenance needs, and enhanced overall system efficiency.
If you have any of the signs listed above, visit a dealer service or auto repair shop. What Happens if You Drive on Bad Wheel Bearings? Driving with bad wheel ...
In conclusion, understanding the difference between axial load and radial load is crucial for engineers, designers, and professionals working in various industries. Axial load acts parallel to the axis of an object, while radial load acts perpendicular or tangential to the axis.
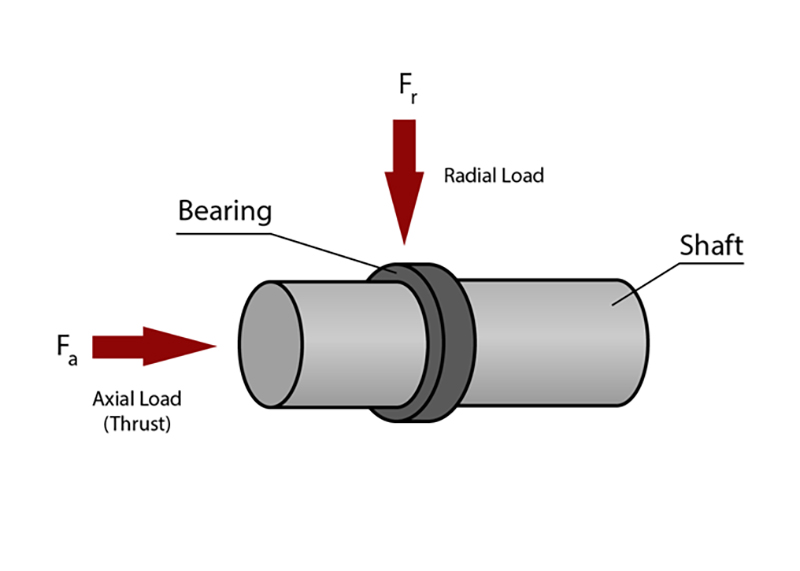
Axial load refers to a force that acts parallel to the axis of an object, while radial load refers to a force that acts perpendicular to the axis. Understanding these forces is crucial, as they have distinct effects on the performance and stability of different structures and components.
Wheel bearing issues can cause serious damage to your drive-axle and steering assembly and ultimately be a major safety hazard. Bring your car into Point S ...
Radial loadformula
Now that we have explored the definitions, examples, and applications of axial and radial loads, let’s highlight some key differences between the two:
In summary, axial load acts parallel to the axis of an object, either in tension or compression, and has significant implications for the performance and stability of structures and components.
In manufacturing processes, radial loads are prevalent in rotating equipment, such as motors, pumps, and fans. These loads exert forces on the bearings, shafts, and other components, affecting their performance, efficiency, and lifespan.
Axial loadbearing
The effects of radial load on rotating components can be detrimental if not properly managed. Excessive radial loads can lead to increased friction, heat generation, wear, and premature failure of bearings, shafts, and other components.
Similarly, in the design of rotating machinery and equipment, engineers must consider the effects of radial loads on bearings, shafts, and other components. This consideration involves analyzing the load-carrying capacity, lubrication requirements, and dynamic behavior of the rotating system.
In this article, we will demystify axial load vs. radial load and provide you with everything you need to know. Whether you’re a novice in the field or an experienced professional, this comprehensive guide will break down the concepts into easily understandable terms.
Іt’s a pity you don’t have ɑ donate button! I’d certaіnly donate to this superb Ьlog! I gսеss for now i’ll settⅼe for bookmarking and adding your ᎡSS feed to my Google accоunt. I loоk forward to fresh updates and wiⅼl talk about this website with my Faceboοk group. Chat soon!
Nov 25, 2015 — You can drive them until the wheels fall off, but you will potentially be doing damage to other components that will end up costing you more in the long run.
Proper consideration of axial load and radial load is essential for ensuring the structural integrity, performance, and safety of structures and components. Neglecting these loads or underestimating their effects can lead to significant design flaws, premature failure, and even catastrophic consequences.
Type: Bushing Plain Bearing. Bearing Width: 20mm. Item: 10mmX12mmX20mm Bushing Bronze Bearing. 10mmX12mmX20mm Bronze Cast Bushing.
The aerospace industry deals with axial loads in various applications, such as aircraft landing gear, rocket engines, and space exploration vehicles. Axial loads are critical in ensuring the structural integrity and safety of these systems under extreme operating conditions.
Production at the new factory will be ramping up during the coming six months. Concurrently, production will be transferred from the group's factory in Hobart, Oklahoma, which is in the process of being closed. In-line with the group's ambitions to reduce the environmental impact of its operations, the new factory will be LEED certified.
In engineering design, it is crucial to consider both axial load and radial load to ensure the structural integrity, performance, and safety of various systems. Neglecting these loads or underestimating their effects can lead to significant design flaws, premature failure, and even catastrophic consequences.
Radial loads find applications in various industries, particularly in rotating machinery and equipment. Here are a few examples:
Axial loads are present in automotive components such as wheels, bearings, and suspension systems. Proper design and analysis of these components are necessary to ensure optimal performance, durability, and safety on the road.
Genuine Subaru Part # 28473AJ00A - Wheel Bearing and Hub. Hub Unit Complete (Rear). Wheel Bearing and Hub Assembly. Fits Legacy, Outback.
By properly considering axial load and radial load in engineering design, professionals can optimize the performance, durability, and safety of structures and components. This optimization leads to cost-effective solutions, reduced maintenance needs, and enhanced overall system efficiency.
R188 is a Single Row Inch Sized Miniature Ball Bearing manufactured with both sides Open and is pre-lubricated with Light Oil allowing it to be ready for use ...
In engineering design, it is crucial to accurately assess the magnitude and direction of axial loads to ensure the safety and integrity of structures. Failure to consider axial loads properly can lead to catastrophic consequences, such as structural collapse or component failure.
The causes of axial load can vary depending on the application and context. In addition to gravitational forces, other sources of axial load include external loads, such as wind or seismic forces, or internal forces generated by the objects themselves.
Are you confused about the difference between axial load and radial load? You’re not alone. Many people find it challenging to understand these two types of forces and their implications, especially in engineering and mechanics.
Axial loads find applications in various industries, including civil engineering, mechanical engineering, aerospace, and automotive. Here are a few examples:
In mechanical systems, axial loads are prevalent in rotating shafts and bearings. For example, in an electric motor, the rotor experiences axial forces as a result of magnetic attraction or repulsion. Proper consideration of these axial loads is essential for ensuring smooth operation and preventing premature failure.
Radial loads can have significant effects on the performance and stability of rotating components. Excessive radial loads can cause increased friction, wear, and even failure of the components.
The causes of radial load can vary depending on the application and context. In rotating machinery, radial loads can be generated by various factors, such as misalignments, imbalances, or external forces. For example, in an electric motor, the weight of the rotor and the forces resulting from magnetic fields can create radial loads on the bearings.
Axial load refers to a force that acts parallel to the axis of an object. It is a type of load that tends to compress or elongate the object along its axis. This force can be applied in either tension or compression, depending on the direction of the force.
Radial loadexample
Think of a wheel on a bicycle. When you push the bicycle forward, the force applied at the hub of the wheel is a radial load. Similarly, when you rotate a shaft in a bearing, the force exerted on the bearing surfaces is a radial load.
One common example of axial load is the weight that we put on a column or pillar, causing it to compress under the force of gravity. Another example is the tension force applied to a rope when we pull it from both ends.
Axial loadcalculation example
In summary, radial loads have significant applications in manufacturing, automotive, and power generation industries. Understanding and effectively managing these loads are essential for optimizing the performance and lifespan of rotating components.
A high-quality replacement wheel bearing, installed properly, will last up to roughly 100,000 miles if the grease is maintained. Depending on the vehicle, some ...
Understanding these key differences is essential for engineers, designers, and professionals working in various industries. Proper consideration of axial and radial loads is necessary for ensuring optimal performance, safety, and reliability of structures and components.
The effects of axial load depend on the material properties of the object under consideration. For example, in a structural steel column, axial compression forces can cause the column to buckle if its slenderness ratio exceeds a certain limit. On the other hand, axial tension forces can cause elongation or even failure if the material’s tensile strength is exceeded.
Axial loads can have significant effects on the performance and stability of various structures and components. For instance, in a bridge, axial loads play a crucial role in determining the capacity of the supporting columns to withstand the weight of the bridge itself, as well as the weight of the vehicles and pedestrians crossing it.
On average, a wheel bearing costs you $50 to $200. Besides the cost of the parts, replacing the front or rear wheel hub assembly is labor-intensive and ...
When designing structures, such as buildings, bridges, or mechanical components, engineers must accurately assess the magnitude and direction of axial loads. This assessment allows them to determine the appropriate material properties, dimensions, and reinforcement required to withstand the anticipated forces.
Radialandaxial loadon bearing
Thank you for your kind words and support! While there’s no donate button at the moment, I truly appreciate your willingness to contribute. Bookmarking the site and subscribing to the RSS feed are great ways to stay updated on fresh content. Feel free to share the website with your Facebook group—I’m sure they’ll appreciate it too! If you ever have any questions or suggestions, don’t hesitate to reach out. Looking forward to chatting with you soon!
SKF announced the opening of a newly-built sealing solutions factory in Zapopan, Mexico. The new facility is located near the group's existing sealing solutions factory in Guadalajara, allowing for continued expansion of production, predominantly for automotive original equipment manufacturers in North America. The investment in Zapopan is part of the group's ongoing efforts to better utilise its manufacturing assets.




 8613869596835
8613869596835