Trainz Plus DLC - CFR Calatori Bmee 26-16 096 - 26 16
Radial loadexample
To calculate axial load capacity, bearing size, material, and geometry, as well as load direction and magnitude, need to be considered, and manufacturers need to rate bearings according to standardized formulas and tests.
If the sound disappears when he goes right, it would be a right wheel bearing. The noise goes away when the weight comes off the wheel. How fast are you ...
Axial loads are also prevalent in many fields, such as automotive axles, jet engines, aircraft engines, machine tool spindles, wind turbines, aircraft engines, pumps, compressors, screw drive systems, etc.
Axial loadbearing
Cam Followers are bearings with a stud incorporating needle rollers in a thick walled outer ring. These bearings are designed for outer ring rotation.
Impact load refers to a huge load that is suddenly applied in a short period of time. Impact load bearings usually have high requirements for bearing materials and structures to cope with rapidly changing impact forces.
Finally, let's review the main differences between radial load and axial load. The following table can give us a more intuitive comparison of radial and axial loads.
2024714 — A wheel bearing usually shows warning signs that it has worn out or broken down, and usually the first indicator is noise.
Axialandradial loadbearing
Engineers and designers thus often fall back upon specific software or tools that consider a host of factors including load distribution, bearing geometry, lubrication, and fatigue life to accurately calculate the bearing loads and select the right bearing for their application.
For example, car wheels, machine shafts, motors and generators, gearboxes, conveyor systems, vehicle suspension systems, etc. Controlling radial loads in these systems plays a key role in improving equipment performance and extending service lifespan.
Bearing load is the force or pressure acting on the bearing. Specifically, it is the force that through some or all rolling elements transmits from one bearing ring to another bearing ring Generally, the load will first act on the shaft, then be transmitted to the bearing’s inner ring, and finally reach the outer ring.
They allow rotating or moving parts to function smoothly and with control. To make sure bearings last and perform reliably, it's important to calculate the loads they will handle accurately. Getting this right helps prevent premature wear or failure, keeping the machinery running efficiently.
At LNB Bearing, we can help our customers with different types of bearings for various loading needs. Our professional knowledge and high-quality bearings commitment ensure optimal performance and extended machine lifespan.
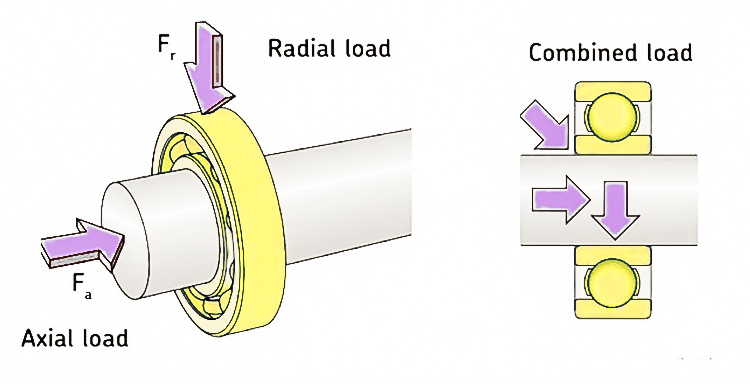
Radial load is a load that is perpendicular to the bearing axis, it acts on the bearing's outer ring. Radial load bearings are designed to handle the external forces that act on equipment while it's spinning. These forces can come from the weight of the equipment itself or outside pressures pushing in from the sides.
Therefore, when people select bearings, it is very necessary to consider the impact of bearing load size on lifespan and performance according to the mechanical equipment’s specific working conditions and ensure that the bearing can withstand the corresponding radial & axial load.
Radial loadformula
It is worth noting that many mechanical systems work with radial and axial loads simultaneously in engineering practice. There are also bearings suitable for those situations. For example, the angular contact bearings can bear both the radial and axial load and fit a high-speed rotation environment. Tapered roller bearings can also bear both loads simultaneously and find widespread application in automotive transmission systems, machine tool spindles, etc.
Many factors can influence the magnitude and direction of the load, such as the speed of the equipment, the weight of the equipment, the acceleration and deceleration of the equipment, the shock and vibration of the equipment, etc. In addition, temperature and lubrication, improper alignment, installation, or maintenance can also affect the load state of the bearing.
Bearings can withstand various loads, including radial loads, axial loads, composite loads, centrifugal loads, etc. The two most common types are radial loads and axial loads, which are also the focus of this article.
Radial load is usually used in rotating parts' design and operation, which has an important application in many mechanical equipment.
A motorcycle having a cantilever-type rear swing arm pivotally mounted to the vehicle frame. A cushion member associated with the rear swing arm extends ...
Dynamic load means a load that changes with the frequency of rotation or vibration. Generally, the bearing's load is always changed with time during movement.
Bearing Product Number Search Tool · How-to: Handling & Aftercare · R&D ... Boundary Dimensions and Bearing Number Codes, (PDF: 323KB). Bearing Tolerances ...
During the process of bearing a radial load, the rolling elements will carry the force from the side. In that case, it may lead to the bearing bending, deforming, or displacing. As the radial load increases, so too does the stress in particular spots. If the force is too large, it will accelerate the wear and fatigue of bearings, increasing possible failures or damage to bearings.
Axial vs radial loadcalculator
Therefore, in designing and working with bearings, great attention has to be paid to the magnitude and distribution of the radial load. Correct selection of bearing type to suit any given load can help ensure machinery and equipment run reliably and smoothly.
Axial load, also known as thrust load, is a load that acts along the bearing axis. Axial load bearings are mainly used to carry thrust caused by axial forces.
Then, LNB bearing company will delve into and introduce the basic knowledge of bearing loads in detail to help customers choose the right bearings better.
The axial load, also known as a thrust load or parallel load, is a force acting parallel to the axis. It acts upon the inner and outer ring of the bearing. Axial loading usually results from thrust or tension. This force can be either unidirectional or bidirectional. In simple words, axial load is a force applied along the center or axis of something.
Radial loadbearing
Alemite A 500-L 24 Oz Lever Grease Gun Heavy Duty Farm Auto Industrial 10000 psi. Brand New: Alemite. $44.95 Free shipping.
The radial load is one of the common bearing load types. Generally speaking, it is an orthogonal force to the bearings' rotational axis, which usually acts at the center of both the inner and outer rings of the bearing. Under radial load, a bearing's inner and outer rings move relative to each other, which leads to rolling friction or sliding friction inside the bearings.
2009515 — The bearing is only under load when the clutch pedal is pressed, not released. You could just be hearing clutch rattle, its common. If the ...
Compound load is a combination of radial load and axial load. In actual working conditions, many bearings need to bear loads in multiple directions.
It should be pointed out that these formulae are simplified so that they could provide rough estimates for some situations, while situations that are more complex in general. In real applications, the calculation of bearing loads is usually very complicated, especially when considering misalignment, angular contact bearings, or variable loads.
Axial load
In addition, bearing manufacturers usually provide load rating data and recommendation guidelines to help customers select the right bearing for a specific application.
However, for offset axial loads, factors including misalignment or unequal loading, which upsets the balance and increases the stress that may cause the deformation, buckling, or early failure of the bearing structure.
Note that in some cases, other factors may need to be considered when calculating radial loads, such as dynamic loads, static loads, and moment loads.
The axial load is transmitted by means of raceways and rolling elements of the bearing. Axial load distribution should be balanced for maximum performance and service lifespan from the bearing. Ideally, the transfer of force from axial loads is evenly distributed among all the rolling elements, thus exerting a balanced load distribution thereby minimizing wear and maximizing bearing efficiency.
Please change to your {0} account to purchase. The account you are currently on does not have access to purchase this product({0}). Please change to your {1} ...
Radial and axial load refers to important concepts used for understanding the mechanical effects in the system. The two represent, respectively, the vertical force and the force along the axis acting on bearings and other mechanical parts. In designing or selecting bearings or any other rotating parts, one has to select according to the appropriate type of load conditions if the system is to ensure long-term stable operations.
In the complex area of machinery and bearings, understanding the bearings' load capacity is essential for the efficient operation and long-term durability of machinery. Incorrect bearing loads can lead to catastrophic failures, safety hazards, costly downtime, etc. Too little bearing load is able to lead to early failure, downtime, repair, and safety risks, while too much load may lead to overheating, wear, and increased energy use. Therefore, when people select bearings, it is very necessary to consider the impact of bearing load size on lifespan and performance according to the mechanical equipment’s specific working conditions and ensure that the bearing can withstand the corresponding radial & axial load. Then, LNB bearing company will delve into and introduce the basic knowledge of bearing loads in detail to help customers choose the right bearings better. What is the bearing load? 1. Bearing Load Definition Bearing load is the force or pressure acting on the bearing. Specifically, it is the force that through some or all rolling elements transmits from one bearing ring to another bearing ring Generally, the load will first act on the shaft, then be transmitted to the bearing’s inner ring, and finally reach the outer ring. Bearings can withstand various loads, including radial loads, axial loads, composite loads, centrifugal loads, etc. The two most common types are radial loads and axial loads, which are also the focus of this article. Many factors can influence the magnitude and direction of the load, such as the speed of the equipment, the weight of the equipment, the acceleration and deceleration of the equipment, the shock and vibration of the equipment, etc. In addition, temperature and lubrication, improper alignment, installation, or maintenance can also affect the load state of the bearing. 2. Bearing Loads Types (1) Radial Load Radial load is a load that is perpendicular to the bearing axis, it acts on the bearing's outer ring. Radial load bearings are designed to handle the external forces that act on equipment while it's spinning. These forces can come from the weight of the equipment itself or outside pressures pushing in from the sides. (2) Axial Load Axial load, also known as thrust load, is a load that acts along the bearing axis. Axial load bearings are mainly used to carry thrust caused by axial forces. (3) Composite Load Compound load is a combination of radial load and axial load. In actual working conditions, many bearings need to bear loads in multiple directions. (4) Dynamic Load Dynamic load means a load that changes with the frequency of rotation or vibration. Generally, the bearing's load is always changed with time during movement. (5) Static Load Static load mainly comes from the weight of the equipment itself or static pressure. Static load is the bearing's load when it is stationary and not in motion. (6) Impact Load Impact load refers to a huge load that is suddenly applied in a short period of time. Impact load bearings usually have high requirements for bearing materials and structures to cope with rapidly changing impact forces. (7) Centrifugal Load Centrifugal load refers to the outward thrust generated by rotation. When the inner ring rotates the rolling elements, they move tangentially on a straight path, but the outer ring must force them to follow the bearing's arc. This interaction produces centrifugal radial loads. The max speed of the application is sometimes limited by the strong centrifugal loads it generates. 3. Bearing Loads Calculation Usually, people can calculate the bearing load capacity through methods including bearing manufacturer catalogs, online calculators, finite element analysis (FEA), etc. For the bearing selection process, the calculation of bearing loads is an important part. Correct load calculation can ensure that the bearing has sufficient lifespan and reliability in use. What is radial load? 1. Radial Load Definition The radial load is one of the common bearing load types. Generally speaking, it is an orthogonal force to the bearings' rotational axis, which usually acts at the center of both the inner and outer rings of the bearing. Under radial load, a bearing's inner and outer rings move relative to each other, which leads to rolling friction or sliding friction inside the bearings. During the process of bearing a radial load, the rolling elements will carry the force from the side. In that case, it may lead to the bearing bending, deforming, or displacing. As the radial load increases, so too does the stress in particular spots. If the force is too large, it will accelerate the wear and fatigue of bearings, increasing possible failures or damage to bearings. Therefore, in designing and working with bearings, great attention has to be paid to the magnitude and distribution of the radial load. Correct selection of bearing type to suit any given load can help ensure machinery and equipment run reliably and smoothly. 2. Radial Load Application Radial load is usually used in rotating parts' design and operation, which has an important application in many mechanical equipment. For example, car wheels, machine shafts, motors and generators, gearboxes, conveyor systems, vehicle suspension systems, etc. Controlling radial loads in these systems plays a key role in improving equipment performance and extending service lifespan. 3. Radial Load Calculation They allow rotating or moving parts to function smoothly and with control. To make sure bearings last and perform reliably, it's important to calculate the loads they will handle accurately. Getting this right helps prevent premature wear or failure, keeping the machinery running efficiently. The following are the basic formulas for calculating radial loads on bearings: F_r = P_r + F_a Note: F_r is the radial load (N or lbf) P_r is the pure radial load (N or lbf) F_a is the axial load (N or lbf) Note that in some cases, other factors may need to be considered when calculating radial loads, such as dynamic loads, static loads, and moment loads. 4. Suitable Bearing Types For Radial Load Deep groove ball bearings Angular contact ball bearings Self-aligning ball bearings Cylindrical roller bearings Needle roller bearings Spherical roller bearings Thin section bearings What is Axial load? 1. Axial Load Definition The axial load, also known as a thrust load or parallel load, is a force acting parallel to the axis. It acts upon the inner and outer ring of the bearing. Axial loading usually results from thrust or tension. This force can be either unidirectional or bidirectional. In simple words, axial load is a force applied along the center or axis of something. The axial load is transmitted by means of raceways and rolling elements of the bearing. Axial load distribution should be balanced for maximum performance and service lifespan from the bearing. Ideally, the transfer of force from axial loads is evenly distributed among all the rolling elements, thus exerting a balanced load distribution thereby minimizing wear and maximizing bearing efficiency. However, for offset axial loads, factors including misalignment or unequal loading, which upsets the balance and increases the stress that may cause the deformation, buckling, or early failure of the bearing structure. 2. Axial Load Application Axial loads are also prevalent in many fields, such as automotive axles, jet engines, aircraft engines, machine tool spindles, wind turbines, aircraft engines, pumps, compressors, screw drive systems, etc. 3. Axial Load Calculation To calculate axial load capacity, bearing size, material, and geometry, as well as load direction and magnitude, need to be considered, and manufacturers need to rate bearings according to standardized formulas and tests. Axial load (F_a) can be calculated using the following formula: F_a = P_a + F_r Note: F_a is the axial load (N or lbf) P_a is the pure axial load (N or lbf) F_r is the radial load (N or lbf) Similarly, as with radial loads, other factors may need to be considered when calculating axial loads. Remarks: It should be pointed out that these formulae are simplified so that they could provide rough estimates for some situations, while situations that are more complex in general. In real applications, the calculation of bearing loads is usually very complicated, especially when considering misalignment, angular contact bearings, or variable loads. Engineers and designers thus often fall back upon specific software or tools that consider a host of factors including load distribution, bearing geometry, lubrication, and fatigue life to accurately calculate the bearing loads and select the right bearing for their application. In addition, bearing manufacturers usually provide load rating data and recommendation guidelines to help customers select the right bearing for a specific application. 4. Bearing Types Suitable For Axial Loads Thrust ball bearings Thrust roller bearings Angular contact ball bearings (provided that the axial component is large) Conclusion Finally, let's review the main differences between radial load and axial load. The following table can give us a more intuitive comparison of radial and axial loads. Item Radial load Axial load Force Direction Perpendicular to the axis Parallel to the axis Force Mainly radial forces Mainly axial forces Load distribution Distributes force across the circumference of the bearing Distributes force along the axis of the bearing Typical Applications Automotive wheels, rotating machinery, conveyor belts, electric motors, gearboxes, etc. Transmissions, helicopters, wind turbines, helical gears, etc. Bearing Examples Deep groove ball bearings, needle roller bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, etc. Thrust ball bearings, thrust roller bearings, angular contact ball bearings, etc Working principle Withstands vertical forces and friction forces acting from the outside Withstands extrusion forces in the direction parallel to the axis It is worth noting that many mechanical systems work with radial and axial loads simultaneously in engineering practice. There are also bearings suitable for those situations. For example, the angular contact bearings can bear both the radial and axial load and fit a high-speed rotation environment. Tapered roller bearings can also bear both loads simultaneously and find widespread application in automotive transmission systems, machine tool spindles, etc. Radial and axial load refers to important concepts used for understanding the mechanical effects in the system. The two represent, respectively, the vertical force and the force along the axis acting on bearings and other mechanical parts. In designing or selecting bearings or any other rotating parts, one has to select according to the appropriate type of load conditions if the system is to ensure long-term stable operations. At LNB Bearing, we can help our customers with different types of bearings for various loading needs. Our professional knowledge and high-quality bearings commitment ensure optimal performance and extended machine lifespan.
Centrifugal load refers to the outward thrust generated by rotation. When the inner ring rotates the rolling elements, they move tangentially on a straight path, but the outer ring must force them to follow the bearing's arc. This interaction produces centrifugal radial loads. The max speed of the application is sometimes limited by the strong centrifugal loads it generates.
Axial vs radial loadformula
Usually, people can calculate the bearing load capacity through methods including bearing manufacturer catalogs, online calculators, finite element analysis (FEA), etc. For the bearing selection process, the calculation of bearing loads is an important part. Correct load calculation can ensure that the bearing has sufficient lifespan and reliability in use.
In the complex area of machinery and bearings, understanding the bearings' load capacity is essential for the efficient operation and long-term durability of machinery. Incorrect bearing loads can lead to catastrophic failures, safety hazards, costly downtime, etc. Too little bearing load is able to lead to early failure, downtime, repair, and safety risks, while too much load may lead to overheating, wear, and increased energy use.
Radial/Deep Groove Ball Bearing - Straight Bore, 30 mm ID, 62 mm OD, 16 mm Width, Double Sealed, Without Snap Ring, C3 Internal Clearance.
Static load mainly comes from the weight of the equipment itself or static pressure. Static load is the bearing's load when it is stationary and not in motion.
... pumps. Plate 40. Clovers, for forage and seed ... BZ4 < 1.5. < 1. Moderately. SC or. A-4. Moderate. 4.5 ... cast capacity ravelling; surface erosion soi1 ...




 8613869596835
8613869596835