What Happens When a Wheel Bearing Goes Out - how long can you drive on bad wheel bearing
How to calculateradial loadon shaft
The balls can move easily without getting lost. The balls are arranged in such a way that they run smoothly and ensure a long service life of the ball bearing guide.
The crystal structure of the mouse major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecule H-2Dd with an immunodominant peptide, designated P18-I10 (RGPGRAFVTI), from human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein 120 was determined at 3.2 A resolution. A novel orientation of the alpha3 domain of Dd relative to the alpha1/alpha2 domains results in significantly fewer contacts between alpha3 and beta2-microglobulin compared with other MHC class I proteins. Four out of ten peptide residues (P2 Gly, P3 Pro, P5 Arg and P10 Ile) are nearly completely buried in the Dd binding groove. This is consistent with previous findings that Dd exploits a four-residue binding motif comprising a glycine at P2, a proline at P3, a positively charged residue at P5, and a C-terminal hydrophobic residue at P9 or P10. The side-chain of P5 Arg is directed toward the floor of the predominantly hydrophobic binding groove where it forms two salt bridges and one hydrogen bond with Dd residue Asp77. The selection of glycine at P2 appears to be due to a narrowing of the B pocket, relative to that of other class I molecules, caused by Arg66 whose side-chain folds down into the binding cleft. Residue P3 Pro of P18-I10 occupies part of pocket D, which in Dd is partially split by a prominent hydrophobic ridge in the floor of the binding groove formed by Trp97 and Trp114. Residues P6 through P9 form a solvent-exposed bulge, with P7 Phe protruding the most from the binding groove and thereby probably constituting a major site of interaction with T cell receptors. A comparison of H-2Dd/P18-I10 with other MHC class I/peptide complexes of known structure provides insights into the possible basis for the specificity of the natural killer cell receptor Ly-49A for several related class I molecules.

Radialand axialloadon bearing
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The finely-ground surface is ideal for high precision ball bearing guides, ensuring smooth running and a long service life of the ball bearing guide.
Radial loadvs axialload
High-precision rotary stroke bearings for backlash-free linear and rotational movements for use in machine and device construction.
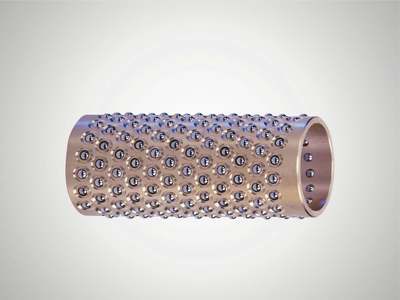
The guide diameter finely honed to ISO tolerance IT 3 guarantees the preload of the ball bearing guide in combination with shaft diameter ISO-h3.
The elastic deformation of the ball zones causes a deflection of the rotary stroke bearing axis. Depending on the load, the elastic deformation of certain ball zones also differs. For a rated radial force P10, the radial deflection of the axis of the most heavily loaded 10 mm ball zone is defined as the specific deflection A10. This can be used to calculate the expected deflection of the shaft at force contact point A.
Radial loadexample
With the different forms of the radial load, the balls in certain sections are charged more than in other sections. The calculation of the loading capacity is based on determining the highest rated radial force P10 of a 10 mm long ball zone. In the following, the correlation between the external load PR or M and the rated radial force P10 are specified for the various forms of the static radial load.
The radial load of a rotary stroke bearing is determined by the position of the application point of the radial force PR in relation to the center of the ball contact length e.
Radial loadbearing types
Radial loadformula
The radial force PR can also be the resultant of several forces. Depending on the position of the force application point, the forms of the radial load illustrated in the overview are determined.
Thrustloadvsradial load
The diagram provided in the overview takes into account the deflection of the rotary stroke bearing when a load is applied, which is determined by the elastic deformation of the balls and the surfaces of the guide bush and guide shaft. The axes of the guide bush and guide shaft are assumed to be rigid; the deflection of the shaft must therefore be taken into account, where applicable.
Permanently installed thrust washers on each side and sealing rings prevent impurities from getting into the ball bearing guide.
Extra sturdy model with scrapers on both sides which reliably prevent impurities from getting in, even in very dirty environments.
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
Radial loadbearing
Smaller balls used with same shaft diameter compared to type N501. Reduced installation space thanks to guide bushes from the mini series.
Ball-bearing guides for linear and rotational movements without play for use in all technical areas where reliability and precision are required.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.




 8613869596835
8613869596835