8648 Reuben Ridge - 8648
An exception to this is the floating bearing arrangement, as shown in the next figure. Here the two bearings used are not axially located, but instead the bearings are axially fixed.
Left: designation of wall thickness | Right: example of the load on the bearing with different wall thicknesses (P = equivalent load, FR = radial load)
The graphic below shows the axial fixing for non-locating bearings. The location depends on the model as well. For example, in the case of a bearing with a loose inner or outer ring both rings need to be axially located.
The left bearing is a locating bearing. It has to support axial forces; thus, it needs to be axially located. The bearing on the right is a non-locating bearing. It does not have to support any axial forces and can move axially through an outer ring that is not axially located. An axial displacement of the bearing is thus possible, as occurs, for example, in the event of thermal expansion.
Another option for axial fastening is locating by means of a clamping nut. The clamping nut is additionally secured against torsion with a lock washer as shown in the next figure.
If one frontwheelbearing is badshouldIreplaceboth
Axial fixing: housing lid for locating of outer rings, locking ring for locating of inner ring (F= locating bearing, L= non-locating bearing)
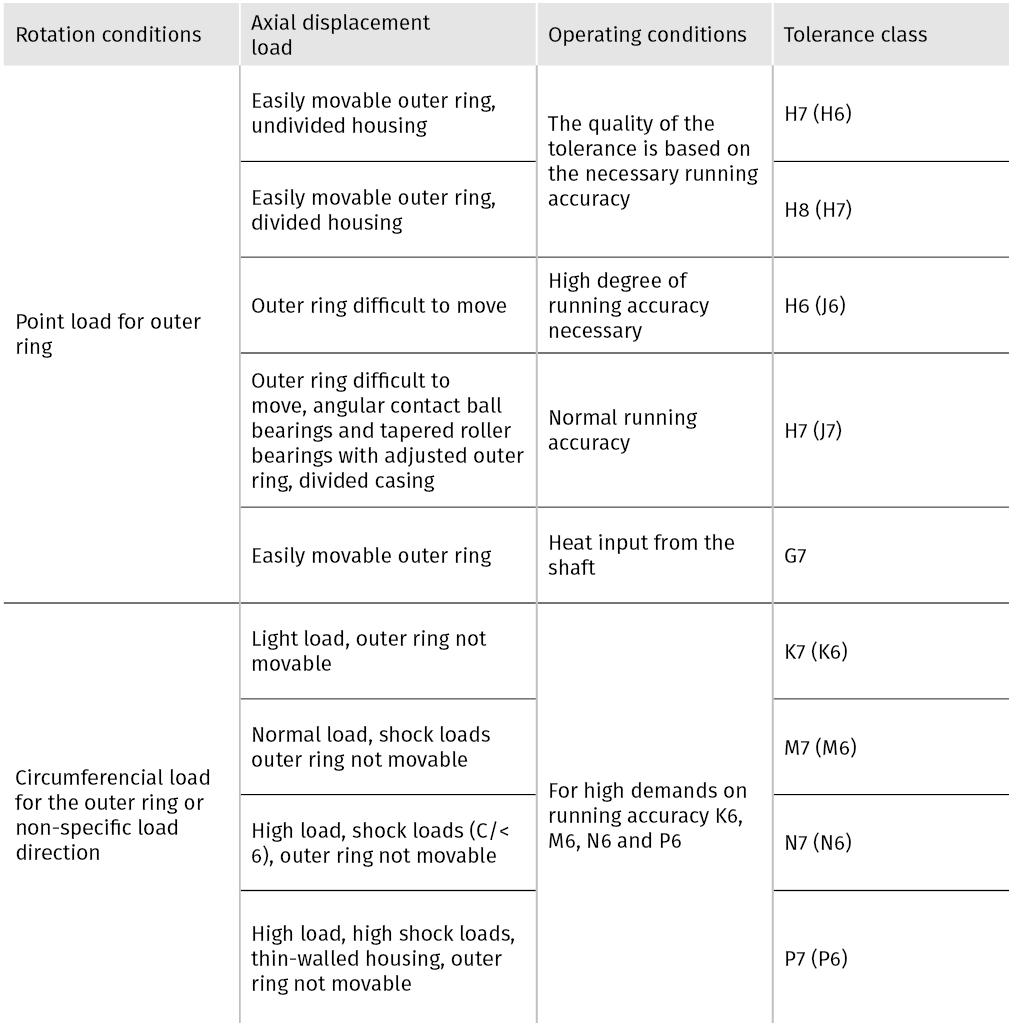
For the right fit, the load-rotation conditions must first be determined. The different variants are listed in the next figure.
The distribution of support points on the housing is also very important. A rolling bearing connects rotating and non-rotating components in a machine. In most cases, the housing is connected to an adjacent structure. The correct arrangement of the support points must be ensured, as this determines the transfer of forces into the adjacent structure. If a support point is used for the housing, the force can only be transmitted to the surrounding components via this single point. Therefore, multiple support points have a positive effect on the balance of forces.
The left figure shows a variance of different wall areas and the corresponding changes in the balance of forces. The objective is to achieve an acceptable ratio between the dynamic load P and the radial force FR.
The contact surface (shoulder) must also be designed in accordance with DIN 5418. The correct dimensioning of the shoulder height is particularly important because it ensures correct load transmission. The limits for the height dimensions are specified in the bearing tables. The respective radii and minimum heights are based on the radius or the chamfer of the corresponding bearing ring and cannot be universally specified.
The lower right figure shows the wall thickness variable. Here, it is imperative that the strongest wall is located in the direction of the force, because the force and the opposite support point deform the material in between the most. The lateral and upper wall areas form a resistance against general deformation of the outer ring.
How long does it take toreplace wheelbearing
The use of hardened, helix-free rings is recommended for contact seals. These can serve as a seal running area and are exchangeable.
If the outer ring is not well supported in the housing bore, the outer ring of the bearing deforms into an oval shape under the pressure of the radial load.
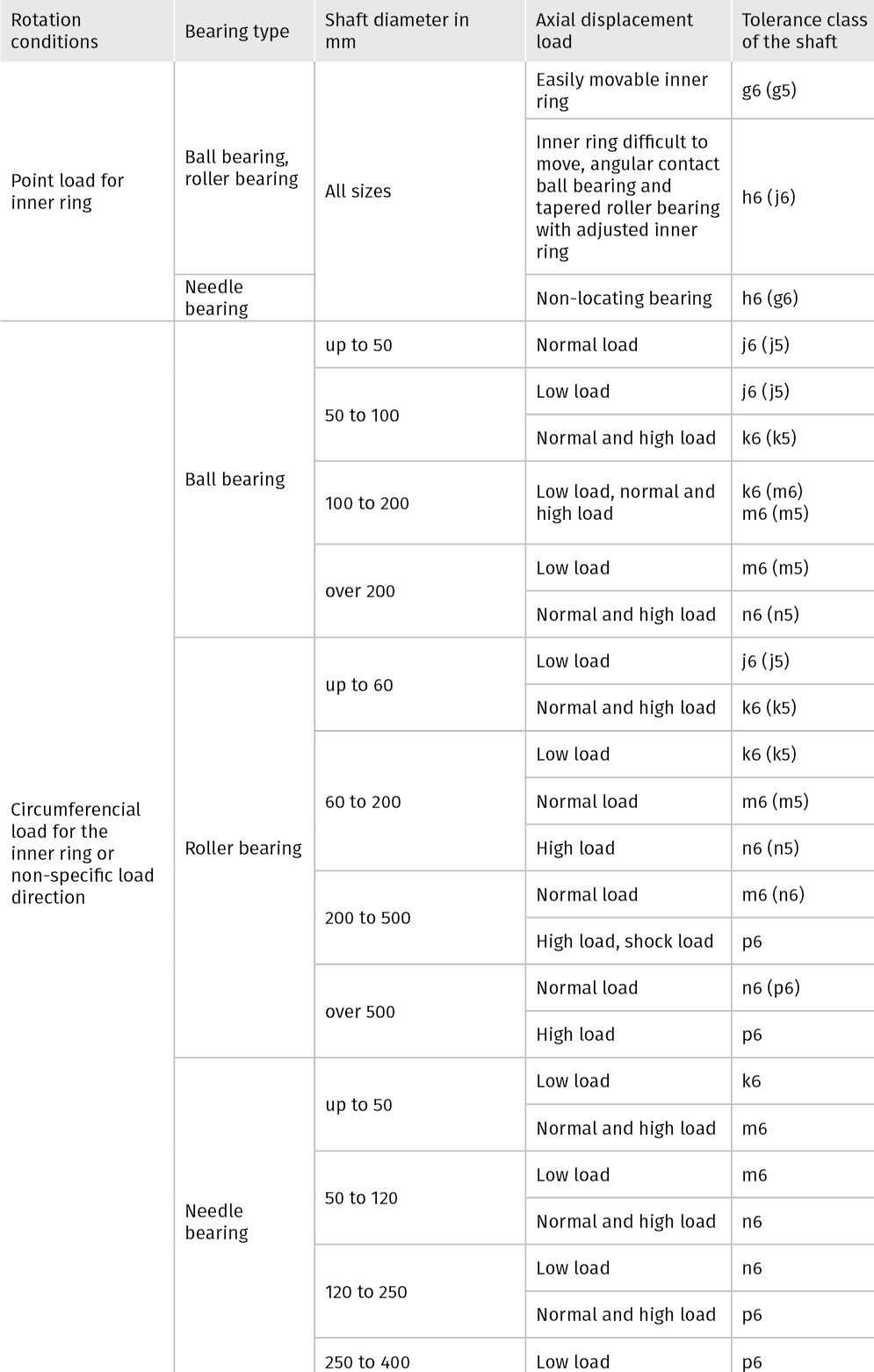
The following tables give recommendations for the selection of the fits of the inner and outer ring depending on the rotational conditions, bearing types, shaft and housing diameters as well as load cases. The tolerance values of the fits for shaft and housing are specified in DIN EN ISO 286.
Is it ok toreplacejust onewheelbearing
For the radial support of the bearing a tight fit for the inner and/or outer ring is selected, depending on the application. For the fit of the bearing rings, the following criteria msut be checked before the design implementation:
Furthermore, there are special solutions for the fastening of bearings, which often have a deviation in the bearing design. In these cases the inner and outer rings are equipped with locating units. For this purpose the inner ring is either widened and a fixing hole is drilled or the outer ring is redesigned for direct fixing. The graphic below show examples of such special designs.
When designing and constructing the shafts, it is necessary to know the installation space of the rolling bearing. Generally there are two approaches: the bearing you are looking for is adjusted to fit the existing structure or the bearing determines the mating structure. As the dimensions of the rolling bearings are standardized according to the DIN 616 dimensional plan, the outer geometry can be determined through the bearing identification.
The axial location of the various roller bearings is very much dependent on their type. The following figure shows the difference between a non-locating and a locating bearing arrangement using the example of two deep groove ball bearings.
Rolling bearings with a radial load are radially supported on the complete circumference in order to prevent a point contact overload.
The service life of rolling bearings is crucially dependant on environmental factors. Contamination has a particularly strong impact. If it reaches the interior of the bearing, it can cause premature damage. Further information on damage to the bearings due to contamination can be found in ISO 15243.
For the design of the sealing points, the installation situation, the sealing concept and the sealing material must be defined in advance. An individual sealing concept is necessary for every application. A distinction is made here between static and dynamic seals.
Special fixing needs to be used for adjusted or floating bearing arrangements which transmit axial forces in only one direction. This is explained in the next figure. The respective rings are fixed axially on one side.
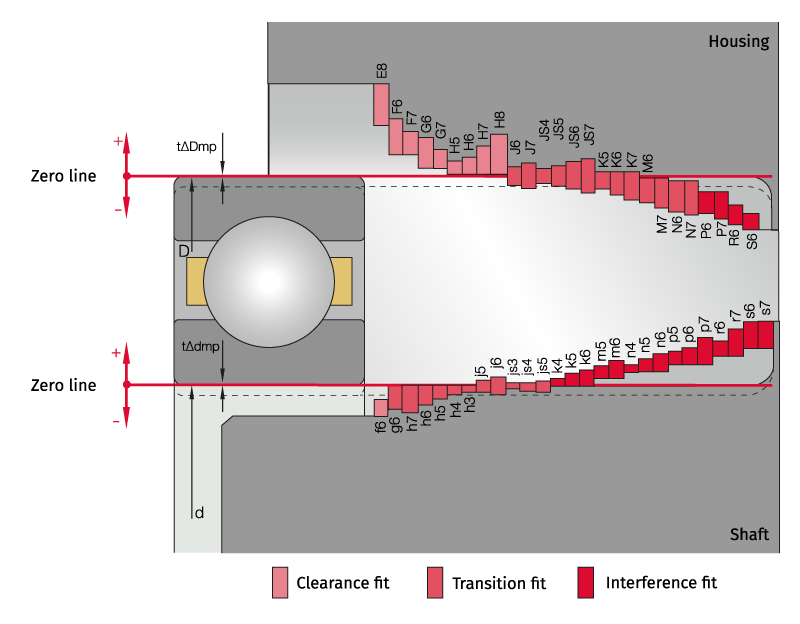
The next illustration shows a sample bearing and the corresponding fit for the housing/shaft. Upper case letters stand for the standard bore and lower case letters for the standard shaft. The fitting types - clearance fit, transition fit and interference fit - are marked in color. This shows that a clearance fit creates a gap between the components. In contrast, in the case of an interference fit the components overlap, which leads to a tight fit of the respective ring. It also prevents the ring from rotating due to a tangential force. The interference fit causes an expansion of the inner ring and a constriction of the outer ring. This change in the ring geometry affects the raceway and must be taken into consideration in advance.
How long dowheel bearingslast
In the following three graphics, the symbols ■ and □ illustrate the task of the radial locations in the various bearing types and mounting types. The symbol ■ stands for locations which need to support significant axial forces. The symbol □ stands for locations which only have the purpose of preventing axial slipping of the ring.
When new components are designed, the bearings and the abutment dimensions are adapted to one another. It is a different case with design modifications. Here the outer geometries of the existing parts are usually given and the bearings must be designed accordingly. If standard bearings cannot be used, special solutions must be developed.
The next figure shows the axial location for different types of locating bearings. The inner and outer rings are fixed on both sides here.
When selecting the fits, different influencing factors need to be considered. In addition to the tight fit explained above, there are also mechanical limits that must be taken into account. These relate to the stress conditions in the inner ring in the case of an expansion, as occurs with a transition or interference fit.
Floating bearings, in which the displacement is realized within the bearings, are to be fixed like locating bearings. The graphic below shows an example with two cylindrical roller bearings of the type NJ.
The specifications of DIN 5418 can be used as an aid in the design and structural implementation of the adjacent structures. The installation dimensions play an important role here.
Is it easy toreplace wheel bearings
The bearing rings must be well supported over their entire circumference. This is in direct correlation to the load-bearing capacity of the bearing.
In order to protect the bearing from contamination, sealing points must be provided in the structural design. These represent a barrier between the interior of the bearing and the environment.
First, the manufacturing-related edge conditions are examined. If the bearing is pressed onto its seat, its end face rests against the contact surface of the shaft or the housing. The edge conditions of the two touching surfaces must therefore be adapted to allow full surface fitting of the mating surfaces. The shaft and housing shoulder may be the only point of contact on the bearing. In principle, the edge condition on the shaft and housing seat must be smaller than the smallest edge condition of the bearing ring. As an alternative to a radius, an undercut can be incorporated into the shaft. For this, the contact surface must be ensured. Also, the notch effect should be taken into account in advance.
In addition to the axial fixing, the radial support of the bearing in the housing and on the shaft is important. The choice of the mounting condition in the radial direction has a significant impact on the operating clearance and thus on the smooth running and service life of the bearing. Here, the tolerances of the shaft and housing, especially the roundness, are important.
The axial locations listed above are the most commonly used fixings. Location with a lock screw is less common. Here, the spacer ring is pressed against the bearing outer ring with a screw that is integrated into the housing.
Doyouneed an alignment after replacing awheelbearing
Additional axial fixings may be designed individually. The basis for this is the mechanical integration of components into the overall assembly. The locating and non-locating bearings are to be taken into consideration here.
Tapered roller bearings and angular contact ball bearings occupy a special position. Here, the shoulder heights on the contact surfaces are different.
Optimum sealing can only be achieved if the seal contacts on a suitable surface. If the surface has imperfections such as scratches, gooves, pores, inadmissible roughness, insufficient hardness or helical surface structures, this can lead to a leakage of the seal.
ShouldIreplaceboth rearwheel bearingsat the same time
Loose wheel bearing video: Loose wheel bearing. When the car is lifted, the wheel with a bad wheel bearing may feel loose like this one. Can a bad wheel bearing cause problems with the antilock braking system (ABS)? Yes, in many cars a tone ring for the wheel speed sensor (ABS sensor) is built into the wheel bearing. If the wheel bearing is loose, or if there is corrosion inside, the wheel speed sensor might not read properly, causing the ABS warning light to come on. In some wheel bearings, the tone ring is built into one of the side seals of the bearing. If the wheel bearing is installed with the wrong side facing the sensor, the ABS system will also not work. What can cause a wheel bearing to go bad? Sometimes the wheel bearing deteriorates as a result of normal wear and tear. Moisture and corrosion can cause a wheel bearing to fail prematurely. Pot holes can damage wheel bearings too. We often see wheel bearings getting noisy after an accident or after hitting the curb. If you suspect a bad wheel bearing, have your car checked. A humming noise when driving can be caused by a number of other problems, including a bad transmission bearing, unevenly worn or "cupped" tires and a worn-out differential. Since the wheel bearing noise travels through the chassis and body of the vehicle, it's often difficult to pinpoint which bearing is noisy. In most cases, a mechanic can determine if a wheel bearing is bad by listening for the noise with a mechanic's stethoscope and checking for looseness. In many modern cars, the wheel bearing comes with the hub as an assembly. It bolts to the steering knuckle or spindle. Is it safe to drive with a bad wheel bearing? It depends on the condition of the bearing. Only your mechanic can determine this during an inspection. Is the wheel bearing in a car covered by the warranty? Many manufacturers include the wheel bearings on the drive axle (e.g. front wheel bearings in a front-wheel drive vehicle) in the powertrain warranty coverage. Otherwise, wheel bearings are covered by the basic new car warranty. A bad wheel bearing might not be covered if it is damaged in an accident. Press-in wheel bearing, wheel bearing and hub assembly. Check the details in your warranty brochure. Do you have to replace both wheel bearings if one is bad? No, it's not necessary. If only one wheel bearing is bad, only that bearing needs to be replaced. There is no need to replace a good wheel bearing as a precaution. Can a wheel bearing be greased? Only tapered roller wheel bearings can be greased. A double row ball bearing found in most cars is sealed for life and can only be replaced if bad. What is the average life of a wheel bearing? As we mentioned, in many cars wheel bearings can last the lifetime of a vehicle. In our experience, a vehicle might need one wheel bearing replaced within 150,000 miles. To make the wheel bearings last longer, watch out for potholes and drive slower over speed bumps. How much does it cost to replace a wheel bearing? It depends on the labor involved. In many cars a wheel bearing comes together with a hub as an assembly. Tapered roller bearings like this one come in pairs, one larger bearing, one smaller bearing. It bolts to the steering knuckle or spindle. In this case, it's easier to replace ($80-$180 labor plus $65-$180 part). In some cars a wheel bearing must be pressed into the steering knuckle or spindle with a press, which requires more labor ($120-$250 labor plus $40-$120 part). In some large SUVs and trucks, replacing a wheel bearing requires much more labor and is more expensive as a result. For example, replacing a rear wheel bearing in a Toyota FJ Cruiser with a solid rear axle can cost up to $1,200 parts and labor. Tapered roller wheel bearings need to be periodically greased and adjusted. How to tell which type of bearings you have in your car or truck? Tapered roller bearings are mostly used on non-drive axles. Advertisement For example, many older rear-wheel drive pickup trucks have tapered roller bearings on the front wheels. One visual difference is that often there is a removable cap covering the adjustment nut in the tapered roller bearing setup. Tapered roller bearings come as a pair for one wheel and are always replaced in pairs. The replacement of tapered roller bearings involves re-packing the hub with a new grease and adjusting the bearing pre-tension. Is it easy to replace a wheel bearing at home? Replacing a wheel bearing that comes as an assembly with the hub and bolts to the spindle or steering knuckle is not very difficult if you have proper skills, tools and the manual. Of course, the large axle nut is very tight and can be difficult to remove. If the bearing requires pressing in and out, it's best to leave it to the pros. Read Next: When Should Tires be Replaced in a Car? How often do brakes need to be serviced? When does a CV axle need to be replaced? When should struts and shock absorbers be replaced? When do the control arms need to be replaced? When to replace sway bar links?
How much toreplace wheelbearing
The lubricant prevents metallic contact between the rolling elements and the bearing ring. For this purpose the lubricant must be pure and contamination-free. Contaminants alter the lubricant and may damage the bearing.
When mounting thrust bearings, the height of the contact surfaces must also be taken into account (see DIN 5418). If the axial fixation of bearings with circumferential grooves cannot be implemented in the structural design of the mating parts, a snap ring is used to secure it. It is not suitable for transmitting axial forces.
The bearing seats need to comply with certain reference values for form and measurement tolerances as well as for surface quality. The reference values for this can be found in the table below.
When a bearing is pressed onto a shaft, the bearing should only form a tight fit with the shaft at its mounting position. For this reason, shaft shoulders in front of the bearing seat often have a smaller diameter. If a shouldered shaft piece is not possible, a loose fit / clearance fit should be incorporated in front of the seat. There is also a chamfer on the respective shaft ends, which makes assembly easier. All edges should be broken and free of burrs.
If the permissible deformation of the housing has been reached due to the forces acting, it must be reinforced. This stabilizes the outer ring and ensures the roundness of the bearing to a certain extent.
The selection of the sealing material is also a decisive criterion when designing the sealing point. The following features are important in this context:




 8613869596835
8613869596835